Principles of management propounded by Henri Fayol are: 1. Division of Work 2. Authority and Responsibility 3. Discipline 4. Unity of Command 5. Unity of Direction 6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest 7.Remuneration of Employees 8. Centralisation and Decentralisation 9. Scalar Chain 10. Order 11. Equity 12. Stability of Personnel 13. Initiative 14. Espirit de Corps!
1. Division of Work:
The entire work is divided into small tasks/jobs and each task/job is performed by a trained specialist.
According to Fayol, “The intent of division of work is to produce more and better work from the same effort. Specialisation is the most efficient way to use human effort.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
According to this principle, work can be performed more efficiently if it is divided in different tasks and each task is then performed by a specialist or trained worker. It is on the basis of this principle that one can find separate departments for finance, production, marketing, human resource etc. in an organisation.
The whole process of any work should be subdivided so that each subdivided part can be performed efficiently and accurately. Division or sharing of work makes people specialists in their respective functions. This principle is very helpful for any organization, be it private, public or government organisation. It enhances overall performance of an organisation because specialists perform consistently well as compared to generalists.
For example, Peter England, a famous brand name among quality shirts has divided its work among various groups. One group is responsible for making collars, other is engaged in stitching buttons, yet another is engaged in packing activities etc.
Advantages of Principle of Division of Work:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(a) It ensures specialisation in the organisation.
(b) It increases efficiency of employees.
(c) It results in increase in output.
(d) It reduces workload
2. Authority and Responsibility:
According to Fayol. “Authority is the right to give orders and obtain obedience and responsibility is the corollary of authority.”
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Authority means power to take decisions and responsibility means obligation to carry out an assigned job. According to Fayol, there should be a balance between authority and responsibility e.g. if any employee has been assigned any responsibility, he must be given sufficient authority to do his job efficiently and vice-versa. Granting authority without giving responsibility will create chances of misuse of power whereas assigning responsibility without providing authority will not enable employees to perform their duty properly. According to Fayol, “The result of authority is responsibility. It is the natural result of authority & essentially another aspect of authority & whenever authority is used, responsibility is automatically born”.
The positive effects of the principle of parity of authority and responsibility are as under:
(i) Builds safeguards against abuse of managerial power.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) Misuse of authority is minimized.
For example, Mr. Abdul Aziz, who is working as sales manager, has to settle a deal with a buyer. He finds out that if he offers a credit period of 30 days he is likely to settle the deal which will bring a net profit of Rs.55 crores to the company. Suppose the company gives power to Mr. Aziz to offer a credit period of only 20 days, he may not be able to settle the deal. Thus obviously, be the manager should granted authority to offer credit period of 30 days which would be in the best interest of the company.
3. Discipline:
Discipline means obedience to organizational rules and employment agreement that are necessary for functioning of any organisation. According to Fayol, discipline requires:
(i) Good supervision at all the levels of management.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) Clear and fair agreement
(iii) Application of penalties judiciously.
In any organisation, many people with diverse profiles aim for achieving common organisational goals. All these people have to function as a cohesive team as per organisational discipline. They all should honour and follow a common system and code of conduct viz. reporting time, leave rules, overtime allowances, bonus etc. Discipline is necessary for the smooth functioning of the organisation.
For example, an agreement has been entered by the management and the labour union whereby the workers have agreed to work an hour extra without additional wages to take out the company from losses and in return the management has promised to increase wages of the worker when the mission is completed. Here, discipline would mean that both workers and the management will fulfill their commitment without any prejudice towards each other.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Discipline is a double-edged tool. On the one hand it enforces orderliness and on the other hand, it motivates them. Personnel entrusted with implementing it are expected to be competent and capable of achieving this balance. Employees must honour the commitment made by them and management must meet its promises viz. increase in wages, declaration of bonus etc. To achieve proper discipline, skilled superiors at all levels, clear and fair agreements and judicious application of penalties etc. are required.
4. Unity of Command:
According to this principle an individual employee should have only one superior from whom he should receive orders and to whom he should be responsible. If an employee receives orders from more than one person at a time it creates confusion and conflict. Thus principle of unity of command avoids confusion and leaves no option for conflict on the part of employees.
For example, Mr. Abdul (Sales Executive), gets instructions from Mr. Parminder (Sales Manager) to sell more to reach targetted sales. At the same time, Mr. Abdul receives orders from Mr. John (Production Manager) to go slow in selling due to shortage of raw materials. In this case, conflict occurs in Mr. Abdul’s mind as to whose instructions he should follow.
Advantages of following this principle:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(i) It helps in preventing the conflict regarding tasks to be done.
(ii) Harmonious relations between superior and subordinates.
(iii) Improves efficiency.
(iv) It helps in fixations of responsibility.
Disadvantages of violating this principle:
(i) Authority is undermined.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) Lack of discipline in the organisation.
(iii) It will result in disturbance and lack of stability.
5. Unity of Direction:
According to this principle, activities having the common goal must have one head and one plan. This helps in bringing unity of action and coordination in an organisation. For example, if a company is manufacturing two different products, it should have two separate divisions or departments for both the products. Each division or department should have their separate incharge, plans and resources.
Advantages of following the principle of Unity of Direction:
(i) It helps in preventing overlapping of activities.
(ii) It ensures unity of action and focused efforts.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iii) It promotes coordination.
6. Subordination of Individual Interest to General Interest:
According to Fayol, organisational interest should be given more priority as compared to individual interest of an employee. An organisation has its own objective while an individual worker has his own individual interest for working in a company. The interests of the group must supersede that of the individual. For the attainment of common goals of an organisation, employees are required to give up carelessness, selfishness, lethargy and their personal interests. They all should focus their efforts on the achievement of common goals.
The positive effects of the principle are as follows:
(i) Ensures coordination between individual and organizational goals.
(ii) Helps in achievement of organizational goals.
(iii) No ego clashes as it gives credit for success of group efforts.
7.Remuneration of Employees:
According to this principle, the remuneration payable to the employees should be fair to both employees and the employer. The employees should get fair wages which ensure at least a reasonable standard of living.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
On the other hand, it should also be within the paying capacity of the business. In short, overall pay and compensation payable to workers should be fair and equitable. This ensures congenial atmosphere between the management and workers. In a healthy atmosphere, satisfied workers put in their best efforts to contribute their maximum.
Advantages of following the principle of remuneration of employees:
(i) This ensures healthy atmosphere and good relations between the employees and the management.
(ii) It ensures smooth functioning of the organisation.
(iii) It motivates employees to contribute their maximum.
8. Centralisation and Decentralisation:
Centralisation is the process of the concentration of power of decision making with one person while decentralisation means dispersal of power of decision making among more than one person. The degree of centralisation or decentralisation depends on how large a company is. Generally, large organisations are more decentralised as compared to others. The panchayat system in our country is a very good example of decentralisation at the national level.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
According to Fayol, “There is a need to balance subordinate involvement through decentralization with managers’ retention of final authority through centralisation”. A company must be properly balanced i.e. it should neither be completely centralized nor decentralized. Hence, depending upon the profile of the organization there must be some element of centralization & decentralization in every organisation.
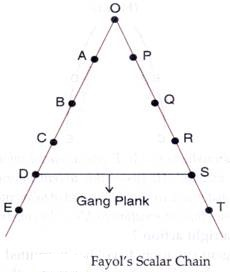
9. Scalar Chain:
According to Fayol, “Organisations should have a chain of authority and communication that runs from top to bottom and should be followed by managers and the subordinates.”
Thus, Scalar chain refers to the formal lines of authority from highest rank to the lowest rank. The principle of scalar chain suggests that there should be a clear line of authority from top to bottom, linking superiors and subordinates at all levels. The scalar chain serves as a chain of command as well as communication. In normal circumstances, the formal communication is required to be made by following this chain.
For example, in an organisation a worker normally cannot directly communicate with the CEO. He has to follow the formal levels i.e. Foreman, Superintendent, Manager, Director etc.
In the given figure the head ‘O’ has two lines of authority under him. One line consists of A-B-C-D-E and another consists of P-Q-R-S-T. Now suppose if D has to communicate with ‘S’ who is also at the same level as D then he has to follow the route D-C-B-A-O-P-Q-R-S according to the principle of Scalar Chain.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Fayol suggested that in normal course of action this chain should be strictly followed. However, in case of emergency D can directly communicate with S through Gang Plank. Gang plank is a shorter route in a scalar chain which allows employees at the same level to communicate with each other directly. It should be ensured that gang plank does not become a normal practice.
It should be used only in case of emergency, to prevent any likely distortion of message and to facilitate expeditious coordination.
10. Order:
According to this principle, in an organisation there should be a suitable place for everything and everyone, and everything and everyone should be at its right place. In other words, we can say that there must be orderliness in the organisation.
According to Fayol, “People and material must be in suitable places at appropriate time for maximum efficiency”. The principle of Order is concerned with proper arrangement of things and placement of people.
The Order can be of following types:
(i) Material Order:
Arrangement of things is called material order. It ensures proper and fixed place for various materials, tools and equipments.
(ii) Social Order:
Arrangement of people is referred to as social order. It ensures proper and fixed place or seat/cabin etc. for each employee in an organization.
Advantages of following this principle:
(t) It results in increase in productivity and efficiency.
(ii) An organisation will function smoothly without any hindrance.
(iii) Minimization of wastage of time/cost in search of men and/or material.
11. Equity:
According to Fayol, “Good sense and experience are needed to ensure fairness to all employees, who should be treated as fairly as possible”. This principle states that managers should be kind and fair towards their workers. All workers should be treated alike and there should be no discrimination on the basis of sex, religion, caste, belief etc. All the employees should be treated equally & impartially.
For example, in a multinational corporation, people of various nations work together in an environment which is free from any kind of discrimination. Equal opportunities for growth and development are available to each employee.
Employees seek to become loyal and devoted if such treatment is given. Subordinates performing similar jobs, like two clerks, should be paid the same wage rate. Similarly, if two employees are latecomers, same treatment should be given to both defaulters. However, Equity does not mean that in an organization equal salary should be fixed for all types of works, instead it obviously has to be based on work profile.
The positive effects of principle are as follows:
(i) Satisfaction of employees leads to boosting up of their morale.
(ii) Development of cordial and harmonious relations among superiors and subordinates.
12. Stability of Personnel:
According to Fayol, “Employee Turnover should be minimized to maintain organisational efficiency”. In an organisation the employees should be selected and appointed after following a due and rigorous procedure. Once they are appointed they should be kept at their positions for a minimum fixed period.
According to this principle, worker should have stability of tenure and should be given sufficient time to show their performance. Moreover, frequent transfers or rotations should also be avoided. If an employee receives transfer order by the time he learns and gets settled in a job it will be leading to wastage of resources and he will not be able to contribute his best to the organisation.
Advantages of following this principle:
(i) Rate of labour turnover will be slow.
(ii) Cost of recruitment, selection and training can be minimised.
(iii)It helps in maintaining organisational efficiency.
13. Initiative:
According to Fayol, “Workers should be encouraged to develop and carry out their plans for improvement”. Initiative refers to the first step taken by the employees towards their self motivation. This principle states that employees at all levels should be given freedom to some extent so that they can come forward and use their skills to achieve expected goals.
It is worth mentioning that while applying the principle of initiative, the established practices of the enterprise should not be bypassed. For creating a healthy environment, employees’ suggestion system should be developed whereby initiatives or suggestions from the employees are invited. Some of those may certainly result in substantial reduction in cost and time.
Advantages of following this principle:
(i) It develops sense of belongingness in employees.
(ii) Employees get satisfaction.
14. Espirit de Corps:
According to Fayol, “Management should promote a team spirit of unity and harmony among employees.” In order to achieve organisational objectives, management should promote team work and coordination. The feeling of ‘I’ should be replaced with ‘We’ in the managers while having a conversation with the workers.
Espirit de corps refers to team spirit i.e. harmony in work group and mutual understanding among workers. It helps to develop an atmosphere of mutual trust and understanding. It also concentrates on the famous saying viz ‘union is strength’.
In case of sports, all team members and in case of armed forces, all personnel play/work for their respective teams. They should not have a thinking that if they win, it is the Captain/Commander alone who will be rewarded. They must work for the team. Similar feeling should be developed among all members of the organization, so that the desired goals of the organization can be achieved with greater effectiveness and efficiency.
Positive effects of ‘espirit de corps’ are as follows:
(i) Develops coordination, mutual trust and belongingness among the employees.
(ii) Team spirit helps to achieve group goals with greater effectiveness and efficiency.