In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Meaning of Project 2. Classification of Project 3. Project Appraisal.
Meaning of Project:
Any proposed activity whose cost and benefit to some extent can be isolated, where cost must be incurred before benefits are known, is known as project. Project can be major or minor. Thus any single proposed activity which involves expenditure and returns, and about which any decision must be made is known as project. Project can have urgent priority or may be of simple in nature but understanding the goal of a project is must.
The goal of the project may be:
i. To make profit irrespective of benefit to many or most of the community.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ii. To employ many of the people of community on the project irrespective of profits.
iii. To make some profit while bringing benefit to many or most of the community.
Any scheme, design, or proposal of something intended or devised to achieve is called project.
There are three basic attributes of project:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
a. A course of action.
b. Specific objectives.
c. Definite time perspective.
Every project has a starting point and an end point with specific objectives.
Classification of Project:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The project can be classified on the basis of its nature.
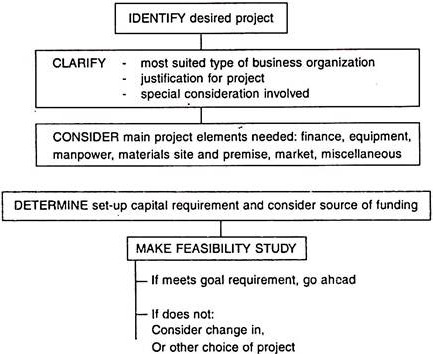
1. Project Identification:
The selection of a right project goes to validate “the trite proposition well begun is half done”. Any project ideas which have a good market can be identified as best project.
Project selection process starts with idea generation. Ideas can be discovered from various internal and external sources.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
These may include:
i. Knowledge of potential customer needs.
ii. Watching emerging trends in demands for certain products.
iii. Scope for producing substitute product.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
iv. Professional magazines.
v. Success stories of known entrepreneur.
Planning a project is a very important task and should be taken up with great care, as the efficiency of the whole project largely depends upon its planning. While planning a project, each and every detail should be worked out in anticipation considering all the relevant provision in advance.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Choosing the Project:
3. Project Implementation:
Next stage in the project cycle is actual implementation of the project for its construction and operation. For proper project implementation, emphasis should be on action as per planning. For this purpose, organization set up and sound project management system should be established so as to manage the projects in a rational and scientific manner, following the latest management principles, tools and techniques. For large international or World Bank aided projects, sometimes consultants are also appointed.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
During the implementation stage of the project, there is need for continuous monitoring to ensure project implementation as per time and cost schedules. For effective monitoring, it is essential to have a good speed and reliability of communication system and establish the dependable information system.
4. Project Monitoring and Control:
Project monitoring is a system procedure to collect and analyses information related to the implementation of the project. The monitoring provides timely information and feedback to the management regarding vital stage in project implementation. Periodic feedback on the progress of the project helps the management to know the achievement of the project and compare it with the targets in order to take appropriate steps for proper implementation of project. As a corrective step, management can correct the lagging time-schedule, synchronize with other related activities and identify other slippages and take remedial measures.
Efficiency of the Monitoring and Control Depends Upon the Efficiency of the Information System:
Monitoring is basically done for parameters, namely project cost originally approved/latest approved estimated cost and project completion/commissioning dates by way of optimum utilization of resources.
Cost Control:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
For the purpose of monitoring the costs, it is not necessary to consider each activity may be small or large, what is necessary is to group individual activities to form work packages, and the records are maintained at the operating level for individual as well as for work packages. Out of these, information regarding work packages only is collected through returns designed for the monitoring system.
Efficiency of monitoring and control of cost also depends upon the proper reporting format and quality of information supplied. Generally, these formats are the cost status, which enable the monitoring manager to know as to how much work has been done, with what cost, and how much cost should have been incurred for this work as per plan (estimate). The frequency of this report is decided according to the requirement of effectiveness of monitoring. This also enables the management to know shortfalls and surpluses in funds position.
5. Project Evaluation:
Projects are evaluated and their performance audit is done with idea of gaining experience for subsequent project in their identification, preparation and appraisal. This ex-post evaluation is very useful in providing experience for future work, since during execution process, the attention is more towards the problems being faced at that time.
These evaluation and completion report both re-estimate the economic rate of return on the basis of actual costs and updated information on operating costs and expected benefits. This evaluation system provides very useful information, supplementing and complementing that provided by the project completion reports.
The idea of evaluation is that, past mistakes are not repeated and new approaches, policies, and procedures are adopted to improve the project performance, reduce cost overruns and implementation delays.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Evaluation of the public projects is based on the benefits and costs analysis instead of the rate of return or extent of profit expected to accrue. Public projects are those projects, which are taken up by the government for the benefit of the public, such as public safety, service, health, education, defence, water supply, roads, irrigation, etc. These projects are financed through government exchequer, and are generally of large in magnitude and multiple in purpose.
Since there is no financial effectiveness measure available for such projects, their evaluation is difficult. Some of the benefits cannot be converted into money value, and usually they do not pay taxes, therefore the criteria for their economic evaluation is different from the private projects. In such cases, general practice is to identify benefits and costs of the projects, and then consider benefit cost ratio as means of economic effectiveness.
6. Preparation of Project Report:
Webster New 20th Century Dictionary defines a project as a scheme, design, a proposal of something intended or devised. In simple words, project report or business plan is a written statement of what an entrepreneur proposes to take up. It is a kind of guide frost or course of action what the entrepreneur hopes to achieve in his business and how is he going to achieve it.
In words, project report serves like a kind of big road map to reach the destination determined by the entrepreneur. Thus, a project report can best be defined as a well evolved course of action devised to achieve the specified objective within a specified period of time. So to say, it is an operating document.
Project report is a written statement of what an entrepreneur proposes to take up. It is a kind of guide or course of action.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
“It is a well-evolved course of action devised to achieve the specified objective within a specified period of time. It is an operating document”.
Significance of Project Report:
i. It is like road map.
ii. It attracts lenders and investors.
Contents of a Project Report:
I. General Information:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
i. Bio-Data of promoter
ii. Industry profile
iii. Plant and machinery
iv. Product details
II. Project Description:
i. Site
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ii. Physical infrastructure
iii. Utilities
iv. Pollution control
v. Communication system
vi. Transport facilities
vii. Other common facilities
viii. Production process
ix. Machinery and equipment
x. Capacity of the plant
xi. Technology selected
xii. Research and development
xiii. Raw material
xiv. Man power
xv. Product
xvi. Market
xvii. Requirement of working capital
xviii. Requirement of funds
xix. Cost of production
xx. Break-even analysis
xxi. Schedule of implementation.
Project Appraisal:
Project appraisal means assessment of a project. It is also a cost and benefit analysis of different aspects of proposed project with an objective to adjudge its viability.
Appraisal of proposed project includes the following:
i. Economic analysis.
ii. Financial analysis.
iii. Technical feasibility.
i. Economic Analysis:
Requirement of raw material, level of capacity, utilization, anticipation sales, anticipated expenses and probable profits.
ii. Financial Analysis:
Assessment of financial requirement both fixed and working.
a. Fixed Assets:
Tangible and material facilities which purchased once are used again and again, e.g. land, building, plant, machinery.
b. Working Capital:
It means excess of current assessors and current liabilities.
c. Current Assets:
These are those assets which can be converted in cash with a period of one week.
Current liabilities are those obligations which can be payable within a period of one week.
“Working capital is that amount of funds which is needed in day today’s business operation.”
Working capital works as a lubricant for any enterprise.
iii. Technical Feasibility:
It is adequacy of the proposed plant and equipment to produce the product within the prescribed norms.
While assessing the technical feasibility of the project the following inputs covered in the project should be taken into consideration:
i. Availability of the land site
ii. Availability of other inputs like water, electricity
iii. Availability of servicing facilitator like machine shop electric shop
iv. Coping with anti-pollution law
v. Availability of work force-skilled, unskilled
vi. Availability of required raw material
7. Common Errors in Project Formulation:
Project formulation is as not so easy. However, the entrepreneur often makes errors while formulating project reports and business plans. Here, we are highlighting the errors widely noticed in project formulation.
i. Product Selection:
It is noticed that some entrepreneurs commit mistakes by selecting a wrong product for their enterprise. They select the product markets, its future demand, and competitive position, and lifecycle, availability of required labour, raw material and technology. Hence, when you are selecting a product, take a comprehensive view.
ii. Capacity Utilization Estimates:
The entrepreneurs usually make over-optimistic estimates of capacity utilization. Their estimates are based on a completely false premise. The estimates are made in complete disregard of present-enterprise performance, prevailing market conditions, competitive atmosphere, the technical snags, etc. A business plan formulated a falls prey to financial jugglery. Hence, avoid such temptations while estimating capacity utilization for your enterprise.
iii. Market Study:
Product production is ultimately meant for eventual sale. Hence, market study of the product assumes importance. Market study continues to be a grey area. But, there are some entrepreneurs who pass by this component of their business plan completely. Based on their nebulous ideas and scanty and scattered information on demand and supply of their proposed product, they conclude that market is just there waiting to be tapped. This is a wrong attitudinal block. Avoid it.
iv. Technology Selection:
The requirement for technology differs from product to product depending upon the nature of products. Swayed by the reported profit margins, the entrepreneurs sometimes plan for a technology not possible to set up within limited financial resources. Thus, in the absence of technology feasibility.
v. Location Selection:
The entrepreneur often makes two types of errors while selecting location for their enterprises. First, they are completely swayed by the government offer of financial incentives and concessions to establish industries in a particular location. This becomes their sole and overriding concern completely disregarding other factors like market proximity, availability of raw materials, manpower and infrastructural facilities. Second, the entrepreneurs select a location for their enterprises merely because it is their home town or they own ancestral land there which is, however, not an appropriate location. Make sure you do not fall prey to such temptations.
vi. Selection of Ownership Form:
Many enterprises fail merely because the ownership form of enterprise is not suitable. Hence, select a suitable form of ownership taking a comprehensive view of the factors affecting the selection of a form of ownership.