In this article we will discuss about:- 1. Definition of Management Control 2. Features of Management Control 3. Management Control System.
Definition of Management Control:
The management function of implementation of strategies is termed as ‘Management Control’. It is defined as “the process by which managers influence the members of the organisation to implement the organisation strategies”.
Features of Management Control:
Management control definition amplifies the following features:
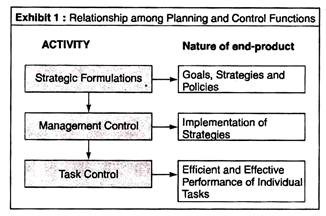
1. Management Control Activities:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Management control function is carried through various managerial activities which are grouped as:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Behavioural Consideration:
Management control aims at influencing people for implementation of strategies by goal congruence. Goal Congruence means that when individual members of organisation seek their personal goals they help to attain the organisation’s goals.
The performance appraisal of managers by results, contributions to goal achievement, development of optimum compensation plans and other incentives are important considerations for promoting goal congruence.
3. Financial and Non-Financial Performance:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Financial and Non-financial performance measures are developed to compare the actual performance against the plans, as overemphasis on financial performance alone may not contribute to the organisation’s long term goals.
Management Control System:
The management control system is made effective through two components, namely:
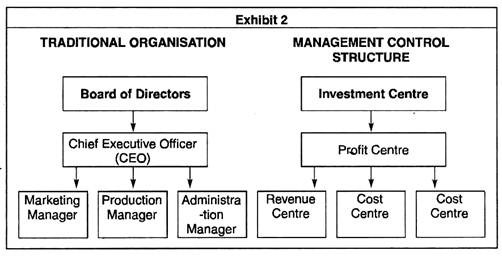
1. Management Control Structure:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The organisation is sub-divided into various sub-units. Each sub-unit is designated as a Responsibility Centre (RC), whose head is called Responsibility Centre Manager.
The Management Control Structure may comprise hierarchy of RCs shown below:
Exhibit 2 shows the comparison of Management Control Structure with traditional organisation structure for the business.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Each RC Manager is responsible for obtaining the optimum relationship between input and output. Each RC is evaluated in terms of efficiency and effectiveness. In some situations the relationship is direct and casual e.g. production department, while in some departments it is difficult to measure the input-output relationship e.g. R&D department, Accounts department etc.
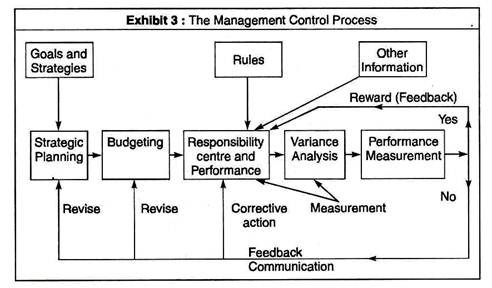
2. Management Control Process:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The steps involved in it are shown in the chart below (Exhibit 3):