In this essay we will discuss about ‘Management’. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Management’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Definition of Management
- Essay on the Concept of Management
- Essay on the Responsibilities and Objectives of Management
- Essay on the Levels of Management
- Essay on the Functions of Management
1. Essay on the Definition of Management:
There is no single definition of management. Management can be styled as “management” i.e., manage men tactfully. The term management can be and often is used in several different ways.
According to Henry Fayol, the father of principles of management, “To manage is to forecast, to plan, to organize, to command and to control”.
According to FW Taylor, “Management is knowing exactly what you want men to do and then seeing that they do in the best and cheapest way”
Mary Parker defines management as “Art of getting things done through people”.
Peter Drucker defines management as “A multi-purpose organ that manages a business and manages manager and manages workers and work”.
John F Mee defines management as “the art of securing maximum results with a minimum effort so as to secure maximum prosperity and happiness for both the employers and employee and give the public the best possible service”.
Richard L. Daft defines management as “the attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efficient manner through planning, organizing, leading, and controlling organizational resources.”
Management is “the process of designing and maintaining an environment in which individuals, working together in groups, efficiently accomplish selected aims”.
Having gone through above definitions of management, now it can be defined as getting things done through others/subordinates. In other words it is a process of various functions like planning, organizing, leading and controlling the business operations in such a manner so as to achieve the objectives set by the organization.
Management: Science or Arts:
Management is both science and arts. Though it is not a perfect art as music or painting. Similarly, it is not a perfect science as physical or chemical science.
Art is bringing about of desired result through application of skill. The management evolves for the application to a specific situation. Intuition and creativity are often the key ingredients of successful managers.
Science, on the other hand, is a systematic body of knowledge acquired by making through observations, experiments and intelligence, which may be verified by researchers. Many theories of management have evolved through experimentation and the results are well structured. Examples are leadership and motivation theory. Many areas of operations management such as forecasting, production planning and control, inventory management, etc., are more towards science. Thus, management is both science and arts. Generally, it is the situation which determines the orientation towards science or art.
2. Essay on the Concept of Management:
The concept of management is not fixed. It has changed according to time and circumstances. The concept of management has been used in integration and authority etc. Different authors on management have given different concepts of management.
The main concepts of management are as follows:
(i) Functional Concept.
(ii) ‘Getting Things Done Through Others’ Concept.
(iii) Leadership and Decision-making Concept.
(iv) Productivity Concept.
(v) Universality Concept.
(i) Functional Concept:
According to this concept ‘management is what a manager does’. The main followers of this concept are Louis Allen, George R. Terry, Henry Fayol, E.F.L. Brech, James L. Lundy, Koontz and O. Donnel, G.E Milward, mcfarland etc.
The functional concept as given by some of the authors is given below:
Louis Allen, “Management is what a manager does.”
James L. Lundy, “Management is principally the task of planning, coordinating, motivating and controlling the effort of others towards a specific objective. Management is what management does. It is the task of planning, executing and controlling.”
George R. Terry, “Management is a distinct process consisting of planning, organizing, activating and controlling performed to determine and accomplish the objective by the use of human beings and other resources.”
Howard M. Carlisle, “Management is defined as the process by which the elements of a group are integrated, coordinated and/or utilized so as to effectively and efficiently achieve organizational objectives.”
Henry Fayol, “To manage is to forecast, and plan, to organize, to command, to coordinate and to control.”
(ii) ‘Getting Things Done through Others’ Concept:
According to this concept, ‘Management is the art of getting things done through others’. It is very narrow and traditional concept of management. The followers of this concept are Koontz and O Donnell, Mooney and Railey, Lawrence A. Appley, S. George, Mary Parker Follet etc. Under this concept, the workers are treated as a factor of production only and the work of the manager is confined to taking work from the workers. He need not do any work himself. Modern management experts do not agree with this concept of management.
Some of these authors have explained this concept in the following words:
Mary Parker Follet, “Management is the art of getting things done through others.”
Harold Koontz, “Management is the art of getting things done through and with people in formally organized groups.” It is the art of creating and environment in which people can perform as individuals and yet cooperate towards attaining of group goals.
J.D. Mooney and A.C. Railey, “Management is the art of directing and inspiring people.”
(iii) Leadership and Decision-Making Concept:
According to this concept, “management is an art and science of decision-making and leadership.” Most of the time managers are busy in taking decisions. Achievement of objectives depends on the quality of decisions. Similarly, production and productivity both can be increased by efficient leadership only. Leadership provides efficiency, coordination and continuity in an organization.
Leadership and decision-making concept as given by some authors is given below:
Donald J. Clough, “Management is the art and science of decision-making and leadership”.
Ralph, C. Davix, “Management is the function of executive leadership anywhere.”
Association of Mechanical Engineers, U.S.A., “Management is the art and science of preparing, organizing and directing human efforts applied to control the forces and utilize the materials of nature for the benefit to man”.
F.W. Taylor, “Management implies substitution of exact scientific investigation and knowledge for the old individual judgment or opinion, in all matters in the establishment.”
(iv) Productivity Concept:
According to this concept, “management is an art of increasing productivity.” Economists treat management as an important factor of production. According to them, “Management is also a factor of production like land, labor, capital and enterprise.” The main followers of this concept of management are John F. Mee, Marry Cushing Niles, F. W. Taylor etc.
The productivity concept, as given by the authors is given below:
Jon, F. Mee, “Management may be defined as the art of securing maximum prosperity with a minimum of effort so as to secure maximum prosperity and happiness for both employer and employee and give the public the best possible service.”
F. W. Taylor, “Management is the art of knowing what you want to do in the best and cheapest way.”
Marry Cushing Niles, “Good management achieves a social objective with the best use of human and material energy and time and with satisfaction of the participants and the public.”
(v) Universality Concept:
According to this concept, “Management is universal”. Management is universal in the sense that it is applicable anywhere whether social, religious or business and industrial. The followers of this concept are Henry Fayol, Lawrence A. Appley, F.W. Taylor, Theo Haimann etc.
According to Henry Fayol, “Management is a universal activity which is equally applicable in all types of organization whether social, religious or business and industrial”.
Megginson, “Management is management, whether it is in Lisbon, or in London or in Los Angeles.”
Theo Haimann, “Management principles are universal. It may be applied to any kind of enterprises, where the human efforts are coordinated.”
3. Essay on the Responsibilities and Objectives of Management:
Management has responsibilities to shareholders, employees, customers and society at large.
(i) To shareholders, management has the traditional responsibility of protection of investment plus the earning of a return on that investment in the long run.
(ii) To employees, management must strive to provide steady, challenging and rewarding opportunities, safe working conditions, and providing for health and other benefits through the working years and even after retirement.
(iii) To customers, management must provide a high quality product at a competitive price and render satisfactory service as required.
(iv) To the Society at large, management has the responsibility of always being a good citizen, taking an interest in the affairs of the general public, complying with the spirit as well as letter of law regarding environmental pollution and conservation.
Management Objectives:
There are basically three management objectives:
i. One objective is ensuring organizational goals and targets are met with least cost and minimum waste.
ii. The second objective is looking after health and welfare, and safety of staff.
iii. The third objective is protecting the machinery and resources of the organization, including the human resources.
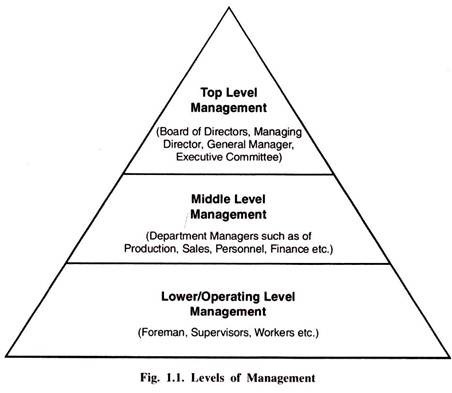
4. Essay on the Levels of Management:
An organization may have different levels of management. the number of levels of management in a particular organization depends on the size of the organization, market value and nature of production based on quality as well as quantity.
A large organization needs different levels of management which has the responsibility to make all the workers get motivated, get organized in order to get the job done within the certain time period and bring a mutual understanding among the workers in different levels of the organization.
The management should provide a clear view about the nature of the work in that particular level, where all the objectives to be accomplished, goals to be achieved. But in order to achieve greater efficiency and maximum productivity, the levels present in the organization should be kept at minimum.
If there are many levels in the organization the cost spend for planning, resources needed for that level will be increased, which might have a great impact on the profit margin of the organization. It might also create problems in communication channels between different personnel of different levels, which would be very difficult to control and coordinate.
According to the experts there are three different levels of management (Refer Fig. 1.1):
1. Top Level Management.
2. Middle Level Management.
3. Lower Level Management.
(i) Top Level Management:
Top level management refers to those who occupy functional positions in an enterprise such as board of directors, managing directors and other key officers who are responsible for smooth and systematic operations of the enterprise.
Top management does not directly execute work. Some of the important functions of top level management are:
a. Setting key objectives, policies and identifying factors essential for the development of the organization.
b. Efficient accomplishment of goals in the organization.
c. Making appointments to the top position in the enterprise such as managers, department heads etc.
d. Reviewing the work of different personnel’s in all levels.
e. Providing overall leadership to the organization.
(ii) Middle Level Management:
Middle level management deals with task of implementing the policies and plans formulated by the top level. It comprises of departmental heads and other executive officers who will lead the group of workers to the planned targets and provide them with necessary resources in order to get the job done.
This group is responsible for the execution and interpretation of policies throughout the organization and for the successful operations assigned to the division or departments. In this level the managers have to plan the operations, issue instructions laid by the top management, collect the resources required and control the work of the men.
Functions to be performed by the middle level management are:
a. Follow the rules and policies formulated by the top management.
b. Motivating personnel for higher productivity and to reward them properly.
c. Recruitment and selection of operative and staff.
d. Collecting detailed analysis report of the department and the personnel’s.
e. Mutual understanding with other departments in the organization.
f. Recommendations to top management for better execution of plans and policies.
(iii) Lower or Operating Level Management:
Operating level management is the lowest level in the organization. It consists of foreman, supervisors, daily labourers etc. Their authority and responsibility in the organization is much less as compared to other workers. They have to follow the rules and guidelines made out by the higher authorities of the enterprise.
The importance of the functions in this level cannot be overlooked. The plan developed by the top level management will fail if the workers in the lower level do not fully realize the work allotted to them and the nature of their work. The quality and quantity of the work done will depend upon the performances of the workers in this level i.e., how hard they work to attain their goals.
Functions to be performed by the lower level management are:
a. Maintaining standards of the quality of the manufactured product.
b. Assigning duties to the workers as per plan and schedules given by the top and middle level management.
c. They are also responsible for maintaining respect and discipline among themselves.
d. To increase the spirit of work among the workers.
5. Essay on the Functions of Management:
Management is a process of getting things done through others. It is a dynamic process consisting of several elements or activities. These activities or elements, which every manager has to perform, are known as functions of management. Various management scholars studies different organizations at different times and identified separate functions of management.
These are:
(i) Planning
(ii) Organizing
(iii) Staffing
(iv) Directing
(v) Controlling
(vi) Co-Ordination
Although co-ordination is not generally regarded as one of the basic management functions, it is extremely important for the success of any organization.
(i) Planning:
Often referred to as the “first” function of management, planning lays the groundwork for all other functions of management. Planning function determines the objectives to be achieved and the course of action to be followed to achieve them. It involves deciding in advance what to do, when to do it, where to do it, how to do it and who is to do it and how the results are to be evaluated. Thus, planning is the systematic thinking about the ways and the means for the accomplishment of predetermined objectives.
Planning is a continuous process and this function is performed at all levels of management. Top managers are involved in strategic planning that sets board, long-range goals for an organization. These goals become the basis for short-range, annual operational planning; during which top and middle managers determine specific departmental objectives that will help the organization makes progress toward the broader, long-range goals.
Planning is a fundamental function of management and all the other functions of management are greatly influenced by planning process. Planning is prerequisite of doing anything. Planning requires decision making i.e., choosing future courses of action from among alternatives. Plans range from overall purposes and objectives to the most detailed actions to be taken. No real plan exists until a decision i.e. a commitment of human and material resources has been made.
(ii) Organizing:
The second function of the management is getting organized. According to Fayol, “To organize a business is to provide it with everything useful to its functioning i.e. men, materials, machines and money”. Thus, organizing is an important managerial function by which management brings together all the resources for the achievement of objectives of the organization.
Management must organize all its resources well before in hand to put into practice the course of action to decide that has been planned in the base function. Organizing involves the assignment of tasks, the grouping of tasks into departments, and the allocation of resources to departments. Managers must bring together individuals and tasks to make effective use of people and resources.
Organization has also been defied as the process of establishing relationships among the members of the enterprise. The relationships are created in terms of authority and responsibility. Each member in the organization is assigned a specific responsibility or duty to perform and is granted the corresponding authority to perform his duty. Thus, organization involves identification and grouping the activities to be performed and dividing them among the individuals and creating authority and responsibility relationships among them.
Organization as a function of management involves the following steps:
a. Determination of activities of the organization.
b. Classification of activities into groups.
c. Assignment of these groups of activities to individuals.
d. Delegation of authority and fixing of responsibility for carrying out such assigned duties.
e. Co-ordination of these activities throughout the organization.
(iii) Staffing:
Organization function of management helps the executives to establish positions and lay down their functional relations to each other. However, it is through staffing function that different positions in the organizational structure are kept manned.
Staffing function is devoted to recruitment, selection, training, placement, compensating, promotion and demotion and finally the retirement of an employee. Thus, staffing is a process of managing the organization and keeping it manned. The sole aim of staffing is to take right person for the right job. It needs manpower planning, job analysis and such other staff functions.
Staffing is concerned with the following three things:
a. Determining manpower requirements i.e., manpower planning.
b. Laying down qualifications for the various jobs to be done i.e. job specification.
c. Recruitment, selection and training of people to perform these jobs effectively and efficiently.
(iv) Directing:
Directing is another of the basic function within the management process. Directing is the use of influence to motivate employees to achieve organizational goals. Managers must be able to make employees participate in achieving an organization’s goals. The directing process helps the organization move toward goal attainment.
As the process of management is concerned with getting work done through and with people, they require continuous encouragement to work effectively. Directing imparts instructions to persons, communicates orders, rules and decisions, motivates, provides leadership and guidance, supervises their work and behaviour, and inspires them towards improved performance.
Directing function consists of three sub-functions:
(a) Leadership:
Leadership is the process of influencing and directing people towards the accomplishment of goal or objective. As leaders, managers have not only to show the way but also to lead the group towards it.
(b) Motivation:
Motivation means inspiring the subordinates with zeal to do work for the achievement of organizational goals. Highly motivated people perform better than unmotivated people.
(c) Communication:
It is the process of passing information and understanding from one person to another. For a manager to be successful, he must develop an effective system of communication so that he may issue instructions; receive the reactions of the subordinates and guide and motivate them.
(v) Controlling:
Planning, organizing, staffing and directing must be monitored to maintain their efficiency and effectiveness. Thus controlling, the last of the five functions of management, is concerned with the act of monitoring each of these functions to evaluate the organizational performance towards meeting goals and objectives. Controlling is the final phase of the management process.
Controlling means monitoring employee’s activities, determining whether the organization is on target toward its goals, and making correction as necessary. Controlling is a function of every manager both at lower and upper level since all have responsibility to execution of plans. Controlling ensures that, through effective directing, what has been planned and organized to take place has in fact taken place.
The control is a measuring and corrective device. It measures performance against goals and plans. Controlling is an on-going process, whereas planning guides the management in the timely use of resources to accomplish specific goals. The control ensures the effective planning.
Controlling function involves the following activities:
a. Establishing standards of accountability.
b. Measurement of work in progress.
c. Interpretation of results.
d. Taking corrective actions.
(vi) Co-Ordination:
Some considers co-ordination as a separate function of management while many others call it as “essence of manager-ship”. The process of co-ordination involves synchronizing individual actions with the goals of the enterprise. In fact, every managerial function represents an exercise in co-ordination.
Thus, planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling, all help the managers to achieve proper co-ordination. Today, organizations have grown in size and in character. A large number of people work there in. So co-ordination has become very necessary.