Here is an essay on the ‘Principles of Management’ for class 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on the ‘Principles of Management’ for school and college students.
Essay # 1. Nature of Principles of Management:
Management is considered to be both a science and an art. Actually it is a social science. The principles of management have been developed on the basis of the experiences of happenings for the past and observations of facts.
Hence these principles have following elements in its nature:
1. Universality:
As Henry Fayol pointed out, principles of management can be used in every type of organisation-business, government, social, military, hospital etc. Thus management principles can be effectively used with equal utility by managers of different organisations and at different levels of authority.
2. Evolutionary:
The body of management principles has been developed on the basis of organised quantitative facts or from the accumulated experiences. Thus these are the expressions of the breadth and depth of the experiences of the leaders of management thought. Therefore they are evolutionary in nature.
3. Flexibility:
Management principles are not a set of rigid prescriptions but are flexible guidelines which can be utilised under different conditions in different ways. One has to keep in mind that enough allowance is needed to use any principle of management depending upon the nature of enterprise, its size, competitive situation, etc.
Principles of management are subject to adjustability. These need to be changed to meet the requirements of the ever-changing conditions. This makes these principles dynamic in nature.
4. Aimed at Influencing Human Behaviour:
Management principles have been evolved, directing towards regulation of complex human behaviour. These principles aim at influencing individual efforts and motivating them towards maximisation of profits with minimum wastage and best possible utilisation of available resources.
5. Limited Application:
Human behaviour is very complex and unpredictable which makes application of management principles difficult.
Essay # 2. Need of Principles of Management:
Proper understanding of management principles is necessary for managers. Such an understanding would make them take more realistic view of the situation.
These are necessary for the following reasons:
1. To Increase Efficiency:
The understanding of the principles helps in setting the objectives of business enterprise and sustained efforts are made possible to get economic results. The established principles of management enable the Managers to make the proper use of the available resources by increasing managerial efficiency.
2. To Highlight the Role of Management:
The principles facilitate in understanding clearly the nature and scope of managerial functions. Principles act as a ready reference for the managers to check whether their decisions are appropriate or not. In short, principles act as a check list to define the scope of managerial activities in practical terms.
3. To Aid in Training of Managers:
The management principles identify and specify the present and prospective scope of management. Management identifies areas wherein managers should be specially trained and management principles provide conceptual framework for systematic training of future managers.
4. To Ensure the Constant Supply of Goods and Services:
Basic principles of management regarding management of finance, personnel, marketing are necessary to make sure that the enterprise does not run out of stock both of raw materials and finished products.
5. To Attain the Social Objectives:
Business has its own responsibility not only to the shareholders but also to its workers, customers, and the society and the government. Management guided by these principles has to endeavour to meet all these responsibilities by increasing efficiency.
6. To Provide Assistance to Researches:
Principles of management would make the continuous study of new findings in the fields of business in particular and related social sciences such as economics, social psychology, etc. possible. It is absolutely essential to carry on researches for finding out innovative methods in the field of marketing, production method, etc.
Essay # 3. Fayol’s Principles of Management:
Henry Fayol (1841 – 1925) is considered ‘The father of administrative management theory’ with focus on development of broad administrative principles applicable to general and higher managerial levels. He was a French mining engineer who rose to the position of leading industrialist and a successful manager.
After his retirement in 1916, he devoted himself for writing a classic book on principles and practice of management entitled Administration industrille Generale which was translated in English as General and Industrial Administration.
As a pioneer of the formal education in management, Fayol wrote that all activities of business enterprises would be divided into six groups:
1. Division of Work:
Fayol advocated division of work to take advantage of specialisation. According to him, “Specialisation belongs to the natural order, the worker works on the same matters, the manager concerned always with the same matters acquire an ability of sureness and accuracy which increases their output.”
This implies the sub division of each task amongst number of persons to make the task simpler and increase output and efficiency. In short, every worker should be assigned only one type of work to attain greater speed and accuracy. This principle applies to all kinds of work, technical as well as managerial.
2. Parity of Authority and Responsibility:
‘Authority’ refers to the right of a superior to get work done from subordinates by giving orders and taking strategic decisions.
‘Responsibility’ on the other hand, refers to the obligation to perform the given task to the best of one’s ability.
Authority and responsibility are coexistent and must go hand in hand. There must be parity between authority and responsibility to regulate the behaviour of the employees. Authority without responsibility leads to irresponsible behaviour while responsibility without authority renders a person ineffective.
3. Discipline:
Discipline is obedience, outward mark of respect and observance of established rules and regulations.
Discipline, being absolutely essential for the smooth running of the business can be classified into two types:
(i) Self imposed discipline, and
(ii) Command discipline
The ultimate success of command discipline lies in its certainty of application.
The best means of facilitating discipline are:
(a) Good supervisors at all levels.
(b) Clear and fair agreements between employees and employers.
(c) Judicious application of penalties
4. Unit of Command:
According to Fayol an employee should receive orders and instructions from one boss and he should be responsible and answerable to him only. Fayol believed that if an employee receives instructions from more than one superior, it would lead to
(i) Confusion and conflict
(ii) Over lapping of orders and duplication of work, and
(iii) Difficulty in pinpointing the responsibility.
Therefore, dual command should be avoided. To sum up, the principle of Unity of Command provides the enterprise a disciplined, stable and orderly existence by creating harmonious and congenial work atmosphere.
5. Unity of Direction:
It means ‘one unit and one plan’. According to this principle, each group of activity with the same objectives must have one head and one plan. This will enable effective co-ordination of individual efforts and energies. In other words, the related activities should be put under one group, ‘there should be one plan of action for them and they should be under the control of one manager.
6. Subordination of Individual to General Interest:
In a business concern, the interest of one employee or a group of employees should not prevail over the common interest of the organisation. In order to achieve supremacy of common goals, the management should set a good example and must be firm in reconciling the differences. Constant supervision must be undertaken in order to prevent any individual from promoting his own interest at the cost of general interest of the firm.
7. Fair Remuneration to Employees:
According to Fayol, the remuneration paid to the personnel of the firm should be fair, proper and satisfactory. To be fair to the employees, wages should be determined on the basis of work assigned, loss of timing, financial position of the business and average wage rates prevailing in the industry.
Logical and appropriate wage rates and the methods of payments boost morale and contentment amongst the staff which an asset to the firm. Fayol recommends that non-financial benefits such as free education, medical and residential facilities should also be provided.
8. Centralisation and Decentralisation:
Centralisation implies the concentration of the authority at the top management. If the subordinates are given more role and importance in the management and organisation, it is termed as decentralisation. According to Fayol, “Everything that increases the importance of subordinates role is decentralisation.”
Absolute centralisation or decentralisation is not feasible, the degree varies on the basis of nature of circumstances, size of undertaking, the type of activities and the nature of organisational structure. Fayol suggests that there should be proper and effective adjustment between centralization and decentralisation in order to achieve maximum results.
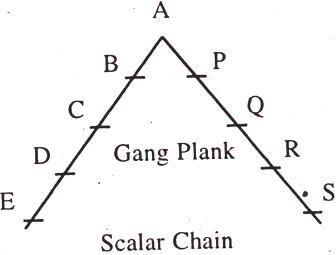
9. Scalar Chain:
Scalar chain means the hierarchy of authority from the highest executive to the lowest one for the purpose of communication. It states the superior- subordinate relationship and the authority of superior in relation to the subordinates at various levels.
It is the unbroken line of command from the top to the bottom of organisational structure wherein orders, instructions, messages, requests, explanations, etc. are communicated between management of workers.
The communication should flow through the established chain of command. However, to facilitate quick communication between two distinct links in the chain, a ‘Gang Plank’ (Direct Contact) may be created by passing the prescribed line of authority. Gang Plank helps to minimise delays and difficulties in communications.
Shows that any communication from D to R will flow upwards to A and then downwards through P, Q and then to R. But to minimise any delays in communication, a Gang Plank between D and R may be created, as shown in the dotted line. Thus, Gang Plank allows two employees at the same level to communicate with each other, with information to the superior.
10. Order:
Order is essentially, a principle relating to management of things and people. There must be material and social order in an enterprise. Arrangement of things which are called ‘Material order’ implies ‘a proper place for everything and everything in its right place’.
Arrangement people refer to as social order means ‘a place for everyone and everyone in its appointed place’. To observe this principle, there is a need for scientific selection of competent personnel and correct assignment of duties to personnel in a good organisation.
11. Equity:
Principle of equity recommends that similar treatment is assured to people in similar positions. It implies fair dealings, equality of treatment and an accommodating attitude amongst the personnel in the undertaking. The application of equity requires mature managerial treatment of the subordinates which ensures healthy and cordial relations between management and subordinates.
12. Stability of Tenure of Personnel:
Fayol emphasised the need to allow enough time to each employee to acquire competence to do his work efficiently. He stressed that the employees should not be moved from their position frequently. Stability of tenure helps to develop a sense of loyalty and attachment amongst the employees whereas unnecessary turnover involves higher costs of selection and training and tarnishes the reputation of the firm.
13. Qualitative:
Qualitative means the freedom to think out and execute a plan. It boosts zeal and energy of employees towards suggesting novel ideas, experiences and more convenient work methodology. According to Fayol initiative is one of the keenest satisfactions for an intelligent man to experience, hence employees at all levels should be encouraged to make all kinds of suggestions to conceive and carry out their plans.
14. Espirit de corps:
Since ‘union is strength’, the management should create team spirit amongst the employees. Harmony and co-operation amongst the staff are a great asset to every organisation. Group efforts should be effectively integrated and channelised towards achievement of best results.