Here is a compilation of essays on ‘Conflict among Employees’ for class 9, 10, 11 and 12. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Conflict among Employees’ especially written for school and college students.
Essay on Conflict among Employees
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Meaning and Definitions of Conflict
- Essay on the Nature and Scope of Conflict
- Essay on the Types of Conflict
- Essay on the Causes of Conflict among Employees
- Essay on the Transition of Conflict
- Essay on the Process of Conflict
- Essay on the Resolution of Conflict
Essay # 1. Meaning and Definitions of Conflict:
To study the dynamics of organizational behaviour, study of conflict management deserves attention. In present corporate environment conflict has become very common phenomenon. Conflict is bad as it has adverse effects on the individual performance.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
If conflict is beyond control it takes a destructive dimension. When employees do not cope-up with the conflict situation, there is an increased absenteeism and exit of employees. It can be so disastrous that can lead to demise of an organization.
On the other hand it has been opinioned that conflict is good for the organization as it produces new ideas, increases competitive spirit, cohesiveness in the team and instils an atmosphere of brotherhood in the organization. This is only possible if ideas are properly channelized and there is proper delegation of authority, empowerment and autonomy in functioning.
Conflict can be defined (Thomas K.A.) as the “process that begins when one party perceives that another party has negatively affected something that the first party cares about.” Conflict must be perceived by either of the parties. Stiff opposition due to incompatibility of organizational goals characterizes it.
Conflict can also be caused due to difference about interpretation of facts or issues involved. Conflict takes an ugly turn and takes a form of violence due to disagreement based on behavioral expectations. It could be covert or overt and can be seen when one observes violent acts of individual in organizations.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Austin et al defines conflict “as a disagreement between two or more individuals or groups, with each individual or group trying to gain acceptance of its views or objective over others.”
Essay # 2
. Nature and Scope of Conflict:
Every organization has its objective. It is further broken down as departmental objectives, group goals and lastly individual goals.
i. When individual interacts with another individual there is perceptual and communication problems that causes misunderstanding and leads to individual conflict situation. It is also true of groups.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ii. Group conflicts indicate the way of inter-group behaviour in an organization. This is more relevant in the Indian context, where inter-union rivalry is most cognigible. Inter-group conflict occurs due to group competition and group cohesiveness. This leads to a feeling of ‘we’ and ‘they’. “We are always right and they are always wrong”.
iii. Hence a beginning of conflict. Aims and objectives of various organizations differ drastically that give rise to greater competition hence a high level of conflict. Conflict can arise between employer and employees, management and workers, one department and another, stakeholders, shareholders, producer and customers and between various trade unions that are often politically motivated.
iv. Schein has pointed out that, this problem exists because as groups become more committed to their goals and norms, they are likely to become competitive with one another and seek to undermine their rivals’ activities, thereby becoming a liability to the organization as a whole. The overall problem, then, is how to establish high productive, collaborative intergroup relations.
v. Michael states that conflict can lead to breakdown in standard mechanism of decision making so that an individual or group experiences difficulty in selecting an action alternative.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The breakdown may be because of competing demands on an individual or group rivalry and competition. There can be vertical and horizontal conflicts; or individual conflict, group conflict and organizational conflict. Conflict can be considered as expression of hostility, negative attitude, aggression and gross misunderstanding. It is caused due to varying interest of individual or groups.
vi. Pondy has described that the term ‘conflict’ is used in four ways to indicate:
1. Antecedent conditions of conflictual behaviour, such as scarcity of resources.
2. Affective states of individuals involved such, as stress, tension, hostility, anxiety etc.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Cognitive state of individuals that is their perception or awareness or conflictual situations.
4. Conflictual behaviour, ranging from passive resistance to overt aggression.
Functional and Dysfunctional Conflict:
Conflict that supports the individual and group goals, which leads to higher performance is called functional conflict while the conflicts that hinders individual or group performance is called dysfunctional conflict. The latter generally takes destructive form. There is thin margin between the two types of conflicts mentioned above.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
While evaluating the impact of conflict on goal achievement, individual perception and effect of group performance should be evaluated. If the conflict contributes towards higher performance then the conflict should be called functional or otherwise dysfunctional.
Conflict can be broadly classified in three types:
1. Task oriented conflict
2. Behavioural conflict
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. And structural conflict or process conflict.
Task conflict relates to the group goals or objectives to be achieved by the group while behavioural conflict relates to individual’s value system, approach, attitude, ego state, skill and norms being followed by him. Studies reveal that most of the dysfunctional conflict falls under this category.
Process conflict is related to how a task is being accomplished in the organization. It is related with various processes, procedures, drills and instructions that are being followed on a particular job.
When individual differs in this regard, conflict arises. This type of conflict can be eliminated to a large extent by following strict discipline in the work procedure and adhering to the rules and regulations.
Positive points of functional conflict are as under:
A. Functional Conflict:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Conflict develops cohesiveness within the group members. A group goal therefore becomes a priority. Individual goals are then relegated to secondary position.
2. Conflict leads to innovation and creativity, as there is competing sprit among various groups.
3. Conflict provides challenging work environment and enhances opportunities for self-development of group that leads to formation of group norms.
4. Enhance work culture leads to up-gradation of various systems within the organization and therefore growth is achieved.
B. Dysfunctional Conflict:
Conflict may turn out to be detrimental and disastrous and having deleterious effects.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Dysfunctional nature of conflict can be identified in the following circumstances:
1. When conflict does not lead to solution.
2. When basic goals of the organization are neglected.
3. People should be treated with due respect. If it is violated and a climate of distrust and suspicion is created people feel defeated and demeaned which develops antagonism and leads to conflict.
4. Conflict may lead to absenteeism and subsequently to increased turn over if not controlled in time.
5. Dual management style may create hatred and lead to dysfunctional conflict.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
6. Disagreement with management may be considered as disloyalty, if this environment prevails, an opportunity for creativity would be lost and employees would lose interest in their job. This would lead to increased conflicting situations.
Essay # 3. Types of Conflict:
i. Inter-Personal Conflict:
Inter-personal conflict relates to conflict between two or more individuals and is probably the most common and recognized form of conflict. Interpersonal conflict is caused due to disagreement over goals and objectives of the organization. These are heightened due to difference of opinion of individuals and when issues are not based on facts.
Every organization is full of unresolved issues, problems and differing situations that leads to conflict. Conflict can also take place between one person of a group with another person of the same group or another group on issues relating to decision-making.
Individuals may have a difference of opinion on selection of a particular course of action that will lead to disagreement and often result in the conflict. It is the merit of the issue, and willingness of members of the organization to accept the others point of view that will avoid the conflict situation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ii. Intra-Group Conflict:
Intra-group conflict relates to values, status and roles played by an individual in the group and the group norms. Individual may want to remain in the group for social needs but may disagree with the methods and procedures followed by the group. The conflict may arise when social changes are incorporated in the group.
When group faces new problems and when values are changed due to change in social environment. Intra-group conflict is like Inter-personal conflict except that the people involved in the conflict episode belong to a common group.
iii. Inter-Group Conflict:
Conflicts between different groups, sections and departments are called inter- group conflict. For example, conflict between production and sales departments over the quality being produced and the customer requirements.
Inter-group conflict causes due to factors inherent to the organizational structure like independence, inconsistency in various policy matter, variance on promotion criteria, reward system and different standards being adopted for different sub-units and departments.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Organizational objectives can only be achieved when all departments work towards attainment of organizational goals. This is possible when interactions between departments are smooth and cordial. Conflict can be avoided by better communication between departments, joint decision making, removing disparity in group goals and paying due respect and displaying concern for other group’s views.
iv. Inter-Organizational Conflict:
Inter-organizational conflict takes place between two dependent organizations. Conflict can take place between government organization, unions and the operating industry. Government organizations function to ensure that minimum standards are followed by the organizations.
Managers must try and reduce inter-organizational conflicts by adopting positive approach and by following strictly, the rules and regulations laid down by the government agencies. Conflict can also take place between seller and buyer organizations.
5. Intra-Organizational Conflicts:
Intra organizational conflict encompasses horizontal, vertical, line-staff and role based conflicts. Let us briefly study these situations.
a. Horizontal Conflict:
Horizontal Conflict is caused due to incompatibility of goals, sharing limited resources and difference in time orientation. It leads to tension, misunderstanding and frustration on the part of both the parties. Horizontal conflict relates to employees or group at the same level. Organizational goal at implementation level vary from department to department.
Finance department may not be able to spare additional amount as may be required by research and development department for new product development that may cause tension, misunderstanding between two individuals or departments. Individuals may not be able to meet the targets of production in given time due to variety of reason that may cause conflict with sales department as the latter would like to flood the market with their product to make the presence felt.
It has been seen that due to increased interdependence of individuals or groups to carry out various functions, situations do arise where there is difference of opinion on issues that cause conflict between individuals or groups.
b. Vertical Conflict:
Vertical conflict refers to conflicts that might take place between different levels of hierarchy. Conflicts between subordinates and superior occur due to incompatibility. It is generally caused because of differences in perception, value system, goals that may be assigned, cognition and difference in individual behaviour. Conflict is also caused due to inappropriate communication between individuals at two different levels.
c. Line and Staff Conflict:
Line and staff conflict has been traditional. Line authority creates product and services and contributes directly towards the revenue generation. While staff authority assists line authority and acts in advisory capacity. Staff and line authority have a different predispositions and goals.
They have different skills and expertise. Since staff authority (managers) is in the chain of command and have a day to day assess to the top boss, have a tendency to dictate terms to the line authority and usually disregard the working knowledge of the line authority.
They have tendency to dominate and disregard the efforts put in by line authority managers. On the contrary staff managers have a technical knowhow and they are able to advice the line authority to cut down cost of production and save on wastage etc. Line authority does not like their advice at times.
Staff managers get frustrated when their suggestions and ideas are not implemented by line managers and hence the cause for conflict. In the process the organizational goals are not achieved as per plans.
Essay # 4. Causes of Conflict:
Communicational Aspect:
Communication is an important process in the organization. Poor communication, passing of an incomplete information to a department may cause conflict because this may have far reaching consequences in attainment of organizational goals. Importance of full and complete communication cannot be over emphasized in the fast moving organizations in the present era of information technology.
Some of the reasons for poor communication are as under:
i. Inadequate communication:
Where too much or too little information is passed from one department to the other.
ii. Filtration effect:
Where end receiver receives very scant information having little or no value.
iii. When information is not received on time:
It must be noted that delayed information has no value as the decision might have already been taken without the information.
iv. Barriers of culture, language.
v. Inadequate training of sender and receiver.
vi. Noise problems.
Essay # 5. Transition of Conflict:
i. Traditional View:
During 1930-40s, conflict was considered to be bad and viewed negatively. It was considered harmful, unnecessary and considered synonymous to violence, destruction and irrational.
The view held that the conflict arose due to poor communication, lack of openness, lack of trust and failure of managers to be responsive to the needs and aspirations of their employees. The view further held that the conflict must be avoided at all costs.
During the same period, the scientific management and administrative school of management that were in the state of evolution, developed such organizational structure where responsibilities had been properly laid down, rules, regulations and policies had been inbuilt in the system.
Thus a proper mechanism was introduced in the management systems and an adequate attention was paid by the managerial staff to ensure that there was no misunderstanding among the employees and that the conflict was avoided.
ii. Human Relations View:
Human relations view, which prevailed between 1940-70 states that conflict is a natural occurrence of individual behaviour and that the conflict cannot be avoided. The theory propagated that we must accept conflict since we cannot eliminate the same. It further states that organizations must lay down proper policy and procedure, set achievable goals.
Have proper communication and thereby avoid stress and strain. Resources should be properly allocated and steps taken to avoid occurrence of conflict. An environment of trust, cooperation, friendship and sharing is built amongst the employees so that increased productivity for the organization is achieved. Avoidance of conflict and trust building is the key for the prosperity of the organization.
iii. Behavioural View:
Behavioural scientists encourage conflict on various grounds. They feel that a group having inter group harmonious relations, peace and cooperation among group members is likely to be non-vibrant, static in nature and can display apathetic attitude towards group members. In this situation the groups are non-responsive. What is required today is innovation, creativity and an ability of the group to meet the social obligations.
Hence there is a need for maintaining minimal level of conflict within the group. This would lead to group being viable: Group members should be self-critical and develop creativity. Minimum level of conflict between the groups would increase competitiveness that will lend itself to higher productivity and increased job satisfaction.
It must be borne in mind that only minimum level of conflict is necessary for it to be beneficial. Behavioral view proposes that because people differ in their attitudes, values and goals, conflict is but a natural outcome in any group of people and that it can be helpful and constructive.
The neo-classicists emphasized the understanding of individual psychology, development of informal groups, informal leadership, and a democratic-participative leadership style so as to avoid conflicts and establish harmony in the organization.
iv. Modern View:
The modern view holds that conflict may be necessary for organizational effectiveness. It is believed that harmonious, peaceful and cooperative groups can become static and uninnovative. Minimum level of conflict that keeps the group alive, self-critical and creative is desirable. Modernists believe that conflict is structural in nature, is inevitable and endemic to the organizational milieu.
It is a product of systems and determined by structural factors and integral to the nature of change. When groups interact there is bound to be difference of opinion and disagreements, which is a cause for conflict. It exists even when there is single individual who is faced with organizational problems like decision making. Conflict should be welcomed and managed effectively.
Some of the positive points of minimum level of conflict are as under:
(a) Conflict should be expressed. By doing so, communication between two groups is restored that promotes growth.
(b) Minimum level of conflict serves as pre-requisite for organizational development. Conflict brings changes.
(c) Conflict helps achieve cohesion within the group that develops group identity and members of the group follow group norms setting aside personal problems. This tendency leads higher level of productivity, sense of identity with the organization and increases group ability to compete with groups and departments.
(d) Poor decisions are detrimental to organizational growth. Minimum level of conflict’ promotes stimulus for analytical thinking, which may challenge views, policies and systems prevailing in the organization. It will lead to reviews hence new policies may be introduced in the organization.
(e) Conflict can serve as power equalizer between two parties. This is clearly observed during management union meetings.
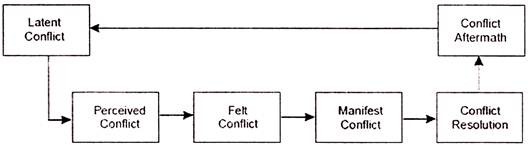
Essay # 6. Process of Conflict:
Pondy developed a conflict process model, which is useful to understand how a conflict starts. He has delineated five steps that he calls as ‘conflict episode’. These are latent conflict, perceived conflict, felt conflict manifest conflict, conflict resolution and conflict aftermath.
The process is adopted and explained Figure below:
i. Latent Conflict:
It is a first stage of conflict when conflict-promoting situations appear on the scene between individuals and groups. In this stage potential conflict inducing forces exist. For example demand for various resources by departments when some may get and be satisfied and others may not get and be dissatisfied. Hence there may exist a situation between two groups. At this stage the seeds of dissatisfaction have been sown.
ii. Perceived Conflict:
When one party frustrate the design of the other party, people perceive that a conflictual conditions exist. For example sales manager may need additional budget for promotional activities which financial manager may not release. The sales manager may attribute lack of finance as potential cause for fall in sales. Thus a conflict between the two may brew. At this stage the conflict does not surface.
iii. Felt Conflict:
At this stage, the conflict is actually felt and cognized. The funds are not released by the finance manager and the problem is being surfaced and there is a likelihood of confrontation.
iv. Manifest Conflict:
In this stage, there is not only recognition or acknowledgement of conflict but also manifestation of conflict by covert or overt behaviour. It is a stage of open dispute. Both parties devise their strategies to face each other. In the above example sales manager may make his point for additional funds for promotional activities especially during festival season.
Finance manager may openly turn down the request since he might have allotted additional funds for procurement of better raw material for production department. Sales manager may argue that better raw material has no meaning unless the facts are brought to the notice of customers, which can only be done through promotional campaign. The debate may be unending and frustrating.
5. Conflict Aftermath:
Once the conflict is resolved between the two parties, there is always a party, which is looser because the resolution is the outcome of win – lose or the compromise strategy, a stage is set for subsequent conflict episodes.
A party, which feels defeated, may start preparations and be on the look-out for the assault to take the revenge. Conflict resolution has been added as an additional box in the figure to elucidate that conflict aftermath is a direct function of the results of the conflict resolution style adopted and exercised in any given situation.
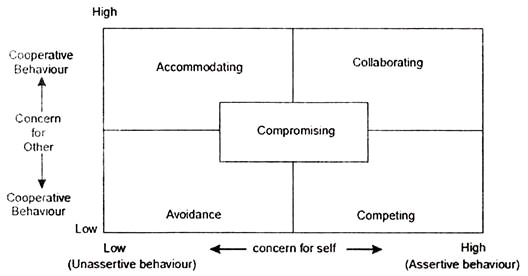
Essay # 7. Resolution of Conflict:
Conflict between parties can be resolved by five different models.
Parties involved may adopt any of the following solutions, which are explained in Figure below:
i. Avoidance:
One or both parties could avoid facing the conflict. The situation pertains to un-cooperative and unassertive behaviour on the part of parties involved. A Party may avoid facing B Party. When situation reaches a point of negligence by A Party, B Party may take advantage of the situation. By avoiding, the individual might side step, postpone or even withdraw from the conflictuating situation.
This strategy is useful when issues involved in conflict are of a very minor nature or when more important issues deserve attention. This strategy suits a manager whose power base is very low and there is no chance of satisfying one’s own concerns. Avoidance strategy should be applied when one feels that people in the organization should cool down so that the issue can be handled at a later date in a better psychological environment.
The issue can also be postponed if additional information is required to be obtained. Avoidance is a poor strategy hence if someone else is able to handle the situation of conflict more effectively, should be allowed to do so.
Managers having high score on avoidance as a strategy of conflict management, may suffer from delayed decision making and hence the loss to the organization. Those who have a low score on avoidance thereby wanting to attend to every single issue may spend lot of time on every trivial issue, hurt people’s feelings and stir hostility in the organization that should be taken care of.
ii. Competing:
This strategy may be adopted when other strategies of conflict resolution are not workable. Competing is also useful m emergencies where quick decisions are required. In this strategy power must be used unilaterally as a weapon when unpopular decisions like termination, pay cuts, layoffs, cost cutting and enforcing discipline are required to be taken. This strategy is based on win-lose principle of managing conflicts.
The managers who are high on power base have an added advantage in using competing strategy because people from opposite side would not dare confront a person who is so powerful. There is a tendency that managers using this strategy should be careful about ‘yes’ men around them.
They should identify conflicting situations and take bold decisions based on win-lose strategy. On the other hand there are managers who are low on competing mode, are likely to feel powerless in many situations. Not realizing that though they have power but they are not comfortable using it.
By trying to use power, one could enhance one’s achievement. Another drawback in scoring low is that such individuals find it difficult to take bold stand on various issues concerning organizations. In situations when a manager is very low on ‘concern for the people’ may postpone vital decisions on matters pertaining to subordinates that may be detrimental to organizational effectiveness.
iii. Collaborating:
Strategy of collaboration involves attempt of one party to work with the other party in cooperative manner and find solutions to the problem for mutual benefits. The strategy involves identification of areas of disagreement, examining the issue in greater detail and a workable solution arrived at, which is for mutual benefit.
This strategy signifies when two sets of solutions are important for both parties to be compromised. Hence finding integrated solution become imperative. This strategy signifies joint efforts, gain for both parties and integrated solutions arrived at by consensual decisions. Sekaran concluded that when people are high on collaborating, they have to be concerned about how they spend their time and other organizational resources.
Collaboration is time and energy consuming. Not all situations need collaborative solutions. Over use of collaboration and consensual decision-making may reflect risk aversion tendencies or an inclination to defuse responsibility.
When people score low on collaborating, they may fail to capitalize on situations, which would benefit immensely from joint problem solving. Also by ignoring the concerns of employees, decisions and policies may be evolved, which make the organizational members both unhappy and uncommitted to the system. The strategy attempts a win— wins solutions to their goals.
iv. Accommodating:
In accommodating mode a person scarifies his own interest for accommodating other person’s interest. It is form of selfless generosity, obeying other person’s point of view. This mode is usually adopted when other person’s view is stronger, you want to achieve goodwill and indicate that you are reasonable. This strategy of conflict resolution is important when you want other person to give at a later date when it favours you.
Sekaran concluded that when people are high on accommodating score they might be differing too much to the wishes of others and pay very little attention to their own ideas and concern even though they may realize that they are not getting the attention they deserve.
This might even lower one’s self esteem in addition to depriving on the influence, respect and recognition from others, since it negates the potential contribution that individuals are capable of making to the organization. While individual low on accommodating score, they should start thinking about whether they lack the goodwill of others and whether others perceive them as unreasonable, uncompromising, rigid and demanding.
v. Compromising:
In conflict situation, compromising is a mode when both parties try to find out some expedient, mutually acceptable solution that sacrifices both the parties partially. In compromising, there is no clear winner or loser. None of the party is fully satisfied as they ration the object of conflict and accept the solution which is not complete to either of the parties. In compromising, there is a possibility of an atmosphere of ‘gamesmanship’ in the work environment.
There is also a possibility of compromising on certain principles of behaviour which is not desirable. Values, ethics, principles and long term objectives of the organization must be protected while adopting compromising. When people are tough to compromise, they find it hard to make concessions and land up in power struggle that must be avoided.
Compromising policies can easily be adopted when competing or collaboration strategy fails. Research indicates that people have underlying disposition to handle conflict in certain ways. Especially individuals have preferences among the five conflict handling intensions.
Their preferences tend to be relied upon quite consistently, and a persons intensions can be predicted rather well from a combination of intellectual and personality characteristics. When confronting conflict situation, some people want to win it at any cost, some wants to find an optimum solution, some want to run away, others want to be obliging, and still others want to “split the differences”.