Emerging Business Opportunities in India!
Emerging Business Opportunities in India # 1. Franchising:
Franchising is a kind of authorization granted to someone to sell or distribute a company’s goods or services in a certain area. The franchiser grants permission to the franchisee to run the business/sell product/offer service for a specified period as specified by a contractual agreement. The franchiser contributes know-how, training, merchandising, and marketing support.
The franchisee backs it up with capital investment and agrees to run the show as per agreed terms. Some examples of today’s popular franchises are McDonald’s, Subway, Domino’s Pizza, Bata, etc. In 2015 Subway was operating in 42000 locations word wide, McDonald’s in 36,368 locations and 7-Eleven Inc. in 56,439 locations.
Essentially, franchising is achieved through two ways:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
i. Product/ Trade Name Franchising:
In product/trade name franchising, a franchisor owns the right to a name or trademark and sells or licenses the right to use that name or trademark to a franchisee (who sells the brand/trade mark in a specific location). The franchising agreement between the two lays down the terms and conditions governing the arrangement. Legally, franchisees do not “own” the franchise they “buy.” They are granted, or awarded, a license that gives them the right to operate and manage their franchise business.
ii. Business Format Franchising:
It involves a more complex relationship in which the franchisor provides franchisees with a full range of services and support, and franchisees sign an agreement to conduct operations in conformity with specific rules laid out by the franchisor.
Working of the Franchising Model-Key Elements:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
i. Franchisor has a reputed brand/trade mark/service
ii. Franchisor holds the licensing right
iii. Franchisor seeks to conquer new markets by investing less
iv. Enters into an agreement with franchisees in other markets
ADVERTISEMENTS:
v. Seeks to grant license for specified periods against royalty payment
vi. Offers marketing, merchandising, advertising and administrative support
vii. Franchisee sets up business using own or borrowed money
viii. Franchisee agrees to pay royalty as long as the contract is alive
ADVERTISEMENTS:
ix. Both parties agree to abide by the contractual obligations for a specified period, and
x. Franchising agreement may be renewed if parties agree to continue the relationship or terminated if they agree to part ways.
Essential Features:
The basic characteristics of a franchising model may be listed thus:
i. Two Parties:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In a franchising deal there is a franchisor (owner of a business model, trade mark/brand willing to grant the right to use the brand/trade mark/business model) and a franchisee (who is willing to pay royalty for getting the right to use the brand/trade mark in a certain area). There can be more than one franchisee in a particular location (E.g. Subway outlets)
ii. Written Agreement:
Both parties enter into a written agreement / contract specifying the terms and conditions of franchising.
iii. Royalty Payment:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
To join the franchisor’s network, the franchisee makes the initial payment. The franchisee continues to make royalty payment as a percentage of sales or profits to franchisor for using the brand/ trade mark during the period of agreement.
iv. Rights and Obligations:
Franchisor assigns the right to use brand/trade mark/business model to the franchisee in a certain area. The franchisee agrees to pay royalty for making use of the same as per the agreement. The agreement specifies what the parties can or cannot do in clear terms, (for example, franchisee being prevented from carrying out a competing business in a different location under a real or disguised name).
v. Support:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The franchisor extends full support to the franchisee in the form of expertise, materials, advertising, etc., so that the franchisee is able to run the show with confidence.
vi. Limited Period:
The franchising agreement is generally for a limited period. If the experiment is successful and both parties want to renew the contract, they can do so if not, it gets terminated.
Advantages of Franchising:
To the Franchisor:
1. Enter new markets
2. Invest less and do more business
ADVERTISEMENTS:
3. Achieve economies of scale when business does well
4. Pass on benefits of increased operations to customers & build goodwill
5. Retain control over business
6. Increase popularity of brand/trade mark by expanding franchising network
7. Steady income in the form of royalties
8. Franchisor owns brand, so works hard to keep it alive and make it popular
ADVERTISEMENTS:
To the Franchisee:
1. Constant help, support from experienced and competent franchisor helps in setting up a successful business and run it properly
2. Gains from the brand name and franchisor’s reputation in several markets where the model worked very well previously
3. Less risky and more profitable business at an affordable prices, and
4. Credit easily available for franchisees who are willing to strike deals with reputed franchisors.
Disadvantages of Franchising:
To the Franchisor:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. The brand name and image may take a dent if franchisee spoils the show
2. Too many franchisees may make it impossible for franchisors to offer requisite marketing, advertising, packaging and administrative support
3. Franchisees learn the tricks of the trade in course of time and set up competing units
4. Franchisees may refuse to pay royalty citing silly reasons or exploiting weak local laws to their benefit.
To the Franchisee:
1. Freedom to run the show independently is missing
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Continual royalty payments may break the back of franchisees in course of time
3. Franchisees may be forced to buy everything from franchisors even though cheaper alternatives are available locally, and
4. Franchisee does not own anything even after running the show for a painfully long time.
Emerging Business Opportunities in India # 2. Outsourcing:
Outsourcing is simply obtaining work previously done by employees inside the company from sources outside the company. It is the contracting out of a company’s non-core, non-revenue producing activities to outside specialists. If someone has specialized in an activity-which is not strategically critical to our business—and is able to do that cost-effectively, it is better to get it from outside.
You get benefited in the form of excellent quality, reliable supply and rock bottom price. You can also focus exclusively on doing what you are good at (the so called mission critical activities)—thereby enhancing your own competitive advantage. For example, Dell outsources the manufacture of its computers. It concentrates all its efforts on enhancing its Web-based direct sales capability and does not dilute its energies on other aspects of the game.
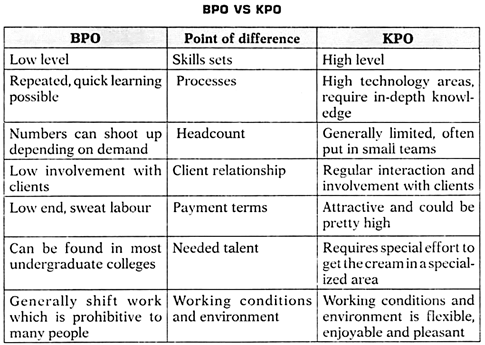
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO):
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) is the act of giving a third party the responsibility of running what would otherwise be an internal system or service. For example, an insurance company might outsource their claims processing programme or a bank might outsource their loan processing system. BPO enables a company to delegate one or more IT intensive business processes to an external provider—who administers and manages the selected process based on a well-defined performance criteria.
The company concentrates on core activities that it is capable of doing in an excellent manner and turns over non-core activities to an outside provider (who is good at doing such things more efficiently) with a view to reduce costs and also improve efficiency.
We can categorize the present BPO services mainly into 7 areas:
1. Customer Support Services- Answering customer queries through voice, e-mail and chat.
2. Technical Support Services- Finding and providing solutions for customer problems related to hardware, software, peripherals, and Internet.
3. Sales and Telemarketing Services- Interacting with customers for selling or promoting products or services.
4. Administrative Support- It includes indexing, form processing, data entry, document conversion, scanning, etc.
5. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) – It includes services such as taking orders, customer service, product support, technical help desk, and market research.
6. Finance and Accounting- It includes internal auditing, travel expenses, time and expense management, credit and debt analysis, collections, invoicing, accounts payable, accounts receivable and billing-dispute resolution.
7. Human Resources and Training- It includes recruitment, training, attrition/ retention, database management, contract-worker management, etc.
Types of BPO:
Mainly three types of BPO outfits exist.
These are:
I. On-Shore BPO- When an enterprise outsources its activities to another company located in the same country.
II. Near-Shore BPO- When activities are outsources to a neighbouring country.
III. Off-Shore BPO- When business processes are outsources to a remote or far off country (e.g. American company outsourcing jobs to India or China).
Critical Success Factors in Outsourcing:
To outsource a business process successfully, the firm should pay attention to the following things, apart from choosing a reliable vendor carefully:
1. Customer Satisfaction:
Once a business process is outsourced to a vendor, he should be able to satisfy the customer and deliver excellent results—much better than what the firm was able to do previously.
2. Definability and Reliability:
The chosen vendor must deliver results on time and on dot without missing any deadlines. He should deliver as per schedules and maintain excellent quality while meeting specifications set by the firm.
3. Cost Effective Solutions:
The vendor must help in saving costs in a significant way. Otherwise, it is no use outsourcing the process from others.
4. Share the Risk:
The vendor must be willing to share the risks and rewards equally. If the vendor fails to meet any of the established service levels or metrics, he should compensate for that and share the risk arising out of such careless or reckless service.
5. Scalability:
Your outsource partner needs to be positioned to meet your growth requirements, so don’t just look at their current capability—look at their ability to scale. Just as you need time to ramp up skills and staff, your outsource provider needs time to react to your needs.
6. Predictability:
How many times have you gone to your favourite fast food franchise expecting to get predictable quality, service, and price, regardless of the town you’re in? It’s the same with any goods or service. Customers expect predictability. Establish metrics around what you define to be “predictable” and measure your outsource provider against then.
7. Competency and Staffing:
Competency and staffing are strategic business issues. Decide whether the environment, set of services or application that you will outsource is deemed “business critical” and whether the intellectual property surrounding it must remain in-house. Once you’ve decided that, it is equally important to assess your ability to adequately staff according to the business needs.
8. Velocity (Reaction to Change):
If you expect lot of changes happening within the business, bring them to the notice of the vendor. Clearly highlight your rate of change and expectations of delivery and quality. This will also allow your outsource partner the ability to staff appropriately. Addressing these factors early on will ensure your greatest chances of success.
What Not to Outsource?
i. Do not outsource core business competencies for which you are known and over which you have got a grip. You derive competitive advantage from the superlative expertise, superior skill, and swift execution of your company’s mission.
ii. Do not outsource issues relating to clients- you need to put out fires, when clients complain; if you leave them to vendors the whole business may collapse
iii. Do not outsource when there’s even a slight threat to confidentiality or security
iv. Do not outsource when it is too expensive- Cost effectiveness is one of the fundamental advantages of outsourcing. If it is proving to be too costly to deliver service effectively, then you should not outsource those activities at all.
v. Do not outsource when outsourcing causes loss of control- You are solely responsible for the outsourced projects—even when are turned over to a vendor. If you lose sight of those projects or lose control then you may have to pay damages to clients when outsourced vendors fail to deliver results.
KPO, MPO and HRO?
When knowledge related and information related processes are outsourced to another location, another company or a subsidiary of the same organization which may be in another country or an offshore location to save cost, it’s is known as Knowledge Process Outsourcing or KPO.
Market Process Outsourcing (MPO) may be explained as outsourcing some or all of the marketing operations thus helping an organisation to focus on its core competencies. MPO gives an organisation to focus attention on client requirements and deliver value accordingly. It can prove to be cost effective. By hiring an MPO company, the organization gets instant and continuous access to qualified and experienced marketing professionals.
Human Resource Outsourcing (HRO) is a process in which a company utilizes the services of a third party to take care of its HR functions. A company may outsource a few or all of its HR related activities to a single or combination of service provides located in offshore destinations like India, China, Philippines.
Benefits of Outsourcing:
i. Focus on Core Competency:
A company is able to focus on its core strengths —such as customer intimacy, product leadership, brand building or operational excellence. The non-core activities may be pushed to outside vendors. By concentrating effort on key drivers that deliver strategic value, a firm is able to improve its competencies and stay ahead of competition.
ii. Lowers Cost:
Outsourcing agencies deliver results (due to specialization) at amazing speeds. Since they are specialists in a field, they know how to bring down costs to bare bone levels. Even if a firm wants to do everything internally, it will not be able to obtain significant savings in cost. Therefore, it makes sense to hire an outside expert to do the job in the best possible manner at rock bottom prices.
iii. No Need to Spend on Infrastructure:
The firm does not have to spend a penny in creating infrastructure needed to handle non-core activities. The systems, processes, resources and people belong to vendors who are eager to serve a client at competitive prices.
iv. Service at an Affordable Price:
The survival of vendors is dependent on how efficiently and effectively they service the cause of clients at an attractive price. In such a tough, competitive scenario a firm would be able to get the services of a specialist at irresistible prices. The firm can tighten the screws and get what it wants on extremely favourable terms.
v. Access to Vendor’s Expertise and Capabilities:
Good and competent providers make extensive investments in technology, people, and methodologies .They acquire expertise by working with many clients facing similar challenges. This combination of specialization and expertise ensures the customers a competitive advantage and helps them to avoid the cost of acquiring technology and training.
vi. Fast, Quick and Effective Deliveries:
Another benefit of outsourcing is that you can make quicker deliveries to customers. Your outsourcing partner will be able to provide faster deliverables and you in turn will be able to make quick deliveries to your customer. Faster deliveries can also help you save on time.
vii. Rely on Vendors for Difficult to Design and Carryout Jobs:
Outsourcing is certainly one option for addressing the problem of managing difficult activities requiring core technical skills. It is essential to remember that outsourcing doesn’t imply abdication of management responsibility nor does it work well as a solution to solve critical and suddenly erupting trouble of a company.
However, a company can outsource only those difficult problems which it understands properly because if the organization doesn’t understand its own requirements, it won’t be able to communicate them to an outside provider.
viii. Reduced Risk:
Tremendous risks are associated with the investments the organizations make. Markets, competition, financial conditions, government regulations and technologies all change quickly. Further, it is very risky to keep up with these changes, especially those in which the next generation requires a significant investment. However, in the context of outsourcing, outsourcing providers make investments on behalf of many clients, not just one and shared investment spreads risk, and significantly reduces the risk born by a single company.
ix. Improved Customer Satisfaction:
With timely deliveries and high-quality services you can impress your customers. Outsourcing can help the firm gain from increased customer satisfaction. It can help a firm remain close to its customers, it can meet all the requirements of customers -in terms of time, cost, delivery, quality etc., and thereby gain an unbeatable competitive advantage.
x. Exploit Time Zone Advantages:
Outsourcing to countries such as India has a time zone advantage. Your night will be India’s day. With this advantage, your outsourcing partner can complete critical work and send it to you the next day. Thus, your work is continued by your outsourcing partner even after your employees go home. This enables the work to be completed much faster and gives your business a competitive advantage. This is one of the benefits of offshore outsourcing.
Limitations of Outsourcing:
i. Dependence:
The firm becomes a victim of over-dependence in course of time. It becomes virtually impossible to get things done if vendors collude and resort to collective actions leading to cost escalation.
ii. Delay:
There is no guarantee that vendors would stick to a tight schedule. If they fail to deliver results, the firm will have to face the music from its own customers. Other than changing a vendor, the firm will not be able to rectify things quickly.
iii. Competition:
The vendor may put up a competing outfit, after getting acquainted with the business environment of the firm. The vendor -after acquiring the tricks of the trade—may get tempted to start operations independently posing a competitive threat to the firm.
iv. Difficult to Get Quality Service at a Remunerative Price:
A further issue is that in many cases there is little that differentiates the service providers other than size. They often provide similar services, have similar geographic footprints, leverage similar technology stacks, and have similar quality improvement approaches. Your outsourcing provider might not be providing services only for your organization. Since your provider might be catering to the needs of several companies, they will not be able to give your company 100% attention.
v. Secrets Leaked Out:
Vendors may begin to leak the secrets of a firm, when relations get spoiled. Any unethical act on their part would destroy the image and reputation of a firm. While outsourcing services such as payroll processing services and tax preparation services, your outsourcing provider will be able to see your company’s confidential information and hence there is a threat to security and confidentiality in outsourcing.
There are three additional dangers in outsourcing which are listed below:
a. Fraud:
When you outsource work there is a very high risk that it is going to be pitted with fraud and corruption, which will indirectly affect the end product that you provide to your customers.
b. Intellectual Property Theft:
This is a major concern even for big companies who are outsourcing tasks. Intellectual property violations end up causing a lot of damage to the repute of a company as well as result in lower revenue. The best example of outsourcing gone wrong is in the case of China, you will find huge number of goods that are excellent copies of big brand being sold at a fraction of the price.
c. Distance from Source and Time Zone:
Factors such as the infrastructure of where you outsource, the distance from the source or the difference in time zone in some cases of outsourcing can affect the value of your business. With more and more businesses worldwide leaping onto the outsourcing bandwagon, it has become a prime concern for startups as well as big companies to conduct due research before deciding to outsource. Outsourcing is a decision that comes after the need to expand faster arises. However, like everything in business, unforeseen costs are also bound to arise in cases of outsourcing.
Emerging Business Opportunities in India # 3. E-Commerce:
E-Commerce or simply electronic commerce, is the process used, to distribute, buy, sell or market goods and services, and the transfer of funds online, through electronic communications or networks. E-commerce allows people to carry out businesses without the barriers of time or distance.
One can buy or sell goods, transfer funds or execute services using the power of Internet. It is a kind of paperless exchange of information that helps anyone to do business online. E-commerce businesses typically sell- (i) physical goods such as books, furniture, appliances etc., (ii) digital goods such as software e-books, music, text, images, video and the like, and (iii) services such as tickets, insurance policies etc.
Features of E-Commerce:
E-Commerce is nothing but doing business electronically, using electronic means such as EDI (electronic data interchange), electronic mail, bulletin boards, fax transmissions, electronic fund transfers and the internet.
It has the following features:
i. Internet is used to conduct business online
ii. Electronic means and platforms are used to conduct business operations
iii. There is electronic trading of goods, services, data, images, information of various kinds
iv. There is also what is called paperless exchange of business information
v. E-Commerce can be carried out by either pure click companies or brick and click companies
vi. E-Commerce has the potential to attract customers anywhere on earth.
Advantages of E-Commerce:
Various advantages of E-Commerce are:
1. Overcome Geographical Limitations:
If we have a physical store, we are limited by the geographical area that we can service. With an ecommerce website, the whole world is our playground. Additionally, the advent of m- commerce, ecommerce on mobile devices, has dissolved every remaining limitation of geography.
2. Gain New Customers with Search Engine Visibility:
Physical retail is driven by branding and relationships. In addition to these two drivers, online retail is also driven by traffic from search engines. It is not unusual for customers to follow a link in search engine results, and land up on an ecommerce website that they have never heard of. This additional source of traffic can be the tipping point for some ecommerce businesses.
One of the most tangible positives of ecommerce is the lowered cost. A part of these lowered costs could be passed on to customers in the form of discounted prices.
Organic search engine traffic, pay-per-click and social media traffic are some of the advertising channels that can be cost-effective.
The automation of checkout, billing, payments, inventory management and other operational processes, lowers the number of employees required to run an ecommerce setup.
This one is a no-brainer. An ecommerce merchant does not need a prominent physical location.
7. Locate the Product Quicker:
It is no longer about pushing a shopping cart to the correct aisle or scouting for the desired product. On an ecommerce website, customers can click through intuitive navigation or use a search box to immediately narrow down their product search. Some websites remember customer preferences and shopping lists to facilitate repeat purchase.
8. Eliminate Travel Time and Cost:
It is not unusual for customers to travel long distances to reach their preferred physical store. Ecommerce allows them to visit the same store virtually, with a few mouse clicks.
9. Provide Comparison Shopping:
Ecommerce facilitates comparison shopping. There are several online services that allow customers to browse multiple ecommerce merchants and find the best prices.
10. Enable Deals, Bargains, Coupons and Group Buying:
Though there are physical equivalents to deals, bargains, coupons and group buying, online shopping makes it much more convenient. For instance if a customer has a deep discount coupon for turkey at one physical store and toilet paper at another, she may find it infeasible to avail of both discounts. But the customer could do that online with a few mouse-clicks.
11. Provide Abundant Information:
There are limitations to the amount of information that can be displayed in a physical store. It is difficult to equip employees to respond to customers who require information across product lines.
Ecommerce websites can make additional information easily available to customers. Most of this information is provided by vendors, and does not cost anything to create or maintain.
12. Create Targeted Communication:
Using the information that a customer provides in the registration form, and by placing cookies on the customer’s computer, an ecommerce merchant can access a lot of information about its customers. This, in turn, can be used to communicate relevant messages.
For Example – If you are searching for a certain product on Amazon.com, you will be automatically show listings of other similar products. In addition, Amazon.com may also email you about related products.
Store timings are now 24/7/365. Ecommerce websites can run all the time. From the merchant’s point of view, this increases the number of orders they receive. From the customer’s point of view, an “always open” store is more convenient.
15. Create Markets for Niche Products:
Buyers and sellers of niche products can find it difficult to locate each other in the physical world. Online, it is only a matter of the customer searching for the product in a search engine. One example could be purchase of obsolete parts. Instead of trashing older equipment for lack of spares, today we can locate parts online with great ease.