After reading this article you will learn about the Meaning and Accounting Treatment for Leasing of Assets.
Meaning of Leasing:
Leasing is an arrangement that provides a firm with the use and control over assets without buying and owning the same. It is a form of renting assets. Lease is a contract between the owner of the asset (lessor) and the user of the asset called the lessee, whereby the lessor gives the right to use the asset to the lessee over an agreed period of time for a consideration called the lease rental.
The lease contract is regulated by the terms and conditions of the agreement. The lessee pays the lease rent periodically to the lessor as regular fixed payments over a period of time.
The rentals may be payable at the beginning or end of a month, quarter, half- year or year. The lease rentals can also be agreed both in terms of amount and timing as per the profits and cash flow position of the lessee. At the expiry of the lease period, the asset reverts back to the lessor who is the legal owner of the asset.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
However, in long-term lease contracts, the lessee is generally given an option to buy or renew the lease.
In the words of Miller, M.H. and C.W. Uptron, “Leasing separates ownership and use as two economic activities, and facilitates asset use without ownership”.
Accounting Treatment of Leases:
(A) In the Books of Lessor:
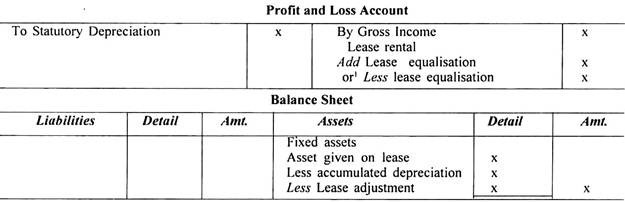
The Lessor will disclose his asset given under lease agreement as an asset given on lease in his balance sheet. The asset will be classified in balance sheet as per method adopted for classification of other fixed assets. All other particulars required as per legal requirements specified in Schedule VI to Companies Act, 1956 should be disclosed in financial statements.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
In income statement lease rentals on actual basis under finance lease should be disclosed separately under head “Gross Income”.
All other charges incurred against the lease rentals should as an annual charge be shown in income statement.
This annual charge should represent recovery of fair value of the leased asset during the term of lease. Annual charge may include as under:
(a) Depreciation (as per the Company Law).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(b) Lease equalisation charge, when annual lease charge is more than statutory depreciation.
A separate lease equalisation account should be opened with a corresponding debit or credit to lease adjustment account as the case may be as under:
Notes:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Statutory depreciation allowed should be shown separately in Profit and Loss Account as shown above in Profit and Loss Account statement.
2. Lease equalisation account should be transferred every year to the Profit and Loss account.
3. Balance standing in lease adjustment account should be deducted from net book values of fixed assets given on lease as shown above in Balance Sheet.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
4. The total amount included under lease adjustment account on account of lease equalisation credits should be disclosed separately.
Basically there are following two methods of accounting for the finance leases:
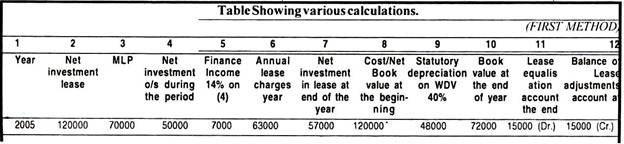
(a) First method:
In first method finance income for the period is calculated by applying the interest rate implicit in the lease to the net investment in the lease during the relevant period.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Illustration 1:
The following particulars are available about a lease agreement.
Cost of leased asset – Rs. 1,20,000
Fair value of leased asset at the inception of the lease (1-1-2005). – Rs. 1,20,000
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The lease term is 4 years.
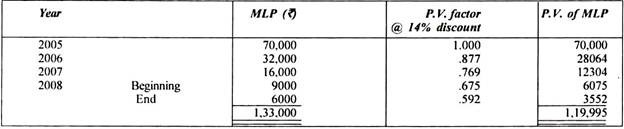
The rental is Rs. 70,000, Rs. 32,000, Rs. 16,000 and Rs. 9,000 respectively in these 4 years, payable in advance every year. The estimated residual value of leased asset at the end of the term of lease is 5% of the cost of the asset. The lessee has right to continue the lease at the end of the aforesaid lease term at a nominal rent. The relevant statutory WDV depreciation is 40%.
Solution:
(i) Calculation of the implicit rate of interest in the lease:
Generally this rate is known to the lessor. However in this case it is not given.
It may therefore be calculated as under:
Since minimum lease payments at the end of the lease, discounted at 14% are equal to the fair value of the leased asset at the inception of the lease, the interest rate implicit in the lease is 14% (by trial and error)
(ii) Gross investment in the lease:
Rs. 1,27,000 + Rs. 6000 = Rs. 1,33,000
(iii) Unearned finance income:
Rs. 1,33,000 – 1,20,000 = Rs. 13,000
(iv) Net investment in lease:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Gross investment – Unearned finance income
Rs. 1,33,000 – Rs. 13,000 = Rs. 1,20,000
Note:
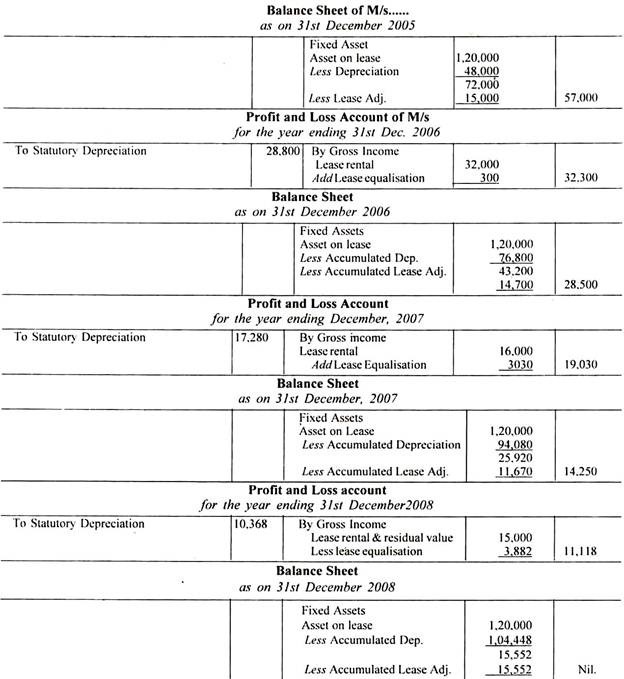
It can be noticed from above calculations that in last year of lease, Lease equalisation account is to be adjusted to the book value of leased asset at the end of the year so as to close the lease.
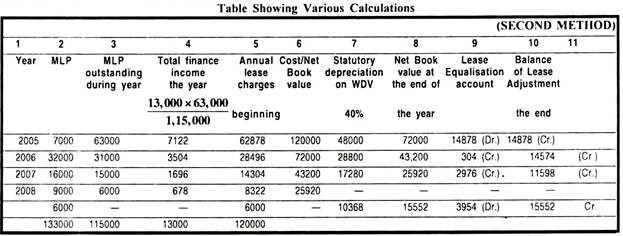
(b) Second Method:
Some lessors use second method which is a very simple method for calculating the finance income for each of the period comprising the term of lease by apportioning the total finance income from the lease in the ratio of minimum lease payments outstanding during each of the respective periods comprising the lease term.
Continuing with same illustration:
Accounting for the lease where finance income is calculated as per the second method.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(i) Calculation of total finance income
Aggregate minimum lease payments = Rs. 1,33,000
Less Fair value of the asset = Rs. 1,20,000
Finance Income = Rs. 13,000
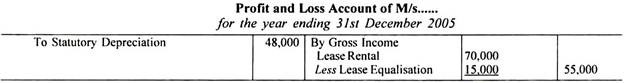
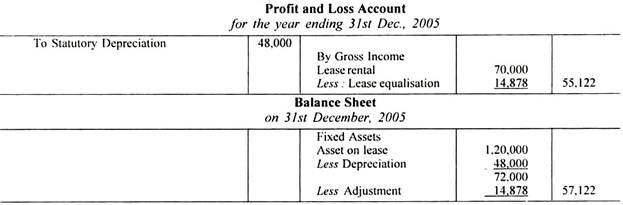
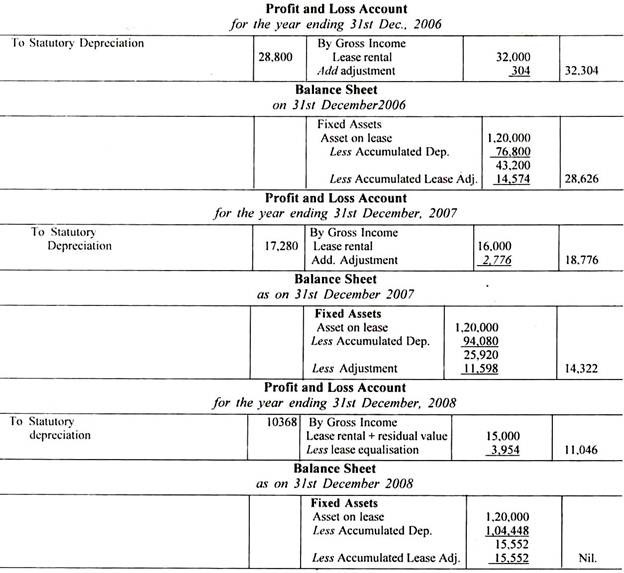
Profit and Loss Account and the Balance sheet of the lessor will disclose as under:
(i) Rental received under lease should be shown under Gross Income in Profit and Loss Account statement.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(ii) The corresponding annual lease charge depreciation etc. are calculated for the term of lease.
Financial statements of lessor will appear as follows:
(B) In the Books of Lessee:
A lease should present assets taken under lease agreement in the category of finance lease by way of a footnote to the accounts. He should disclose future obligations of the lessee as per lease agreement.
Lease rentals should be shown on accrual basis. The relevant charges should be worked out with reference to the terms of the lease agreement. The excess of lease rentals paid over the amount accrued in respect there of should be treated as prepaid lease rent and vice-versa.