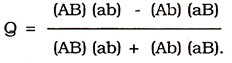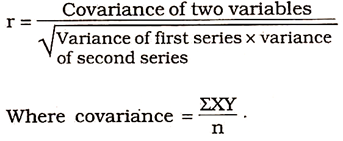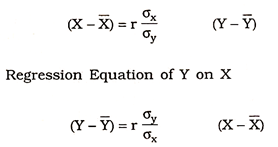A well-designed marketing information system consists of four major components: 1. Internal Accounting System 2. Marketing Intelligence System 3. Marketing Research System 4. Marketing Science System.
Components of Marketing Information System # 1. Internal Accounting System:
In this system the marketing executive receives the historical data from accounting books on sales, costs, inventories, receivable, payables, cash inflows and outflows, funds flows and so on making comparative studies. A firm makes transactions of different types with many persons and institutions.
It is not possible for accountant or anyone to put memory of all the transactions in serial order with brief particulars. So there was felt need for any scientific system which can systematically record all economic transactions and provide the net economic results and position after a specific time. For this basic purpose accounting system is adopted.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The Concept and Forms of Accounting:
In the words of committee on Terminology of the American Institute of Certified Public Accounts, “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transaction and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character and interpreting the results thereof.”
Accounting is a discipline with the recording, analysis and forecasting of income and wealth of business. Generally it records in money terms the flow of economic values of any institution’s economic events.
The following are the main objectives of accounting:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(i) To ascertain the results of operation i.e. profit or loss;
(ii) To ascertain the financial position of business;
(iii) To provide control over assets like cash, capital, stock and others;
(iv) To help the management in its decision-making actions;
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(v) To replace the limitation of human memory.
To fulfill these objectives various branches or forms of accounting have been developed.
The chief branches among these are following:
1. Financial Accounting:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The aim of this accounting branch is to ascertain the profit or loss made during a specific period and the financial state of affairs at the end of the period. Basic financial accounting procedures are journal, ledger, trial balance and final accounts.
2. Cost Accounting:
Its aim is to ascertain the cost incurred for various activities and to enable management for cost control. Costing is the technique and process of cost ascertainment of products or services for the presentation of suitably arranged data for the control and guidance of the management. The methods of cost accounting are—job costing, operation costing, process costing, contract costing, uniform costing etc.
3. Management Accounting:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Here the aim is to supply the management significant and necessary informations in order to assist it in the discharge of various functions such as decision-making, planning, organising, controlling, etc.
Various emerging techniques such as depreciation accounting, funds and cash flow analysis, budgetary control, managerial costing, standard costing, revaluation accounting, zero base budgeting, ratio analysis, human resource accounting, social accounting, inflation accounting, corporate reporting, responsibility accounting; are used in management accounting.
4. Tax Accounting:
There are different tax provisions for sole trade, partnership, company and other organisations. Tax accounting is used to ascertain the various taxes as income tax, wealth tax, gift tax, for various tax payers.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
However, for marketing information mainly financial accounting data based on double entry system are meaningful. In the western world the double entry system was developed by Lucas Pacioli in the 15th century in Italy. The Indian system of accounting has been in use for a very long time and is based on the double entry system; though its origin is not known. The books are known as ‘Bahis’ which are maintained in Indian languages.
Strength and Weakness of Accounting MkIS:
Factors leading to the increasing importance of accounting MkIS are as follows:
1. Record keeping;
ADVERTISEMENTS:
2. Proper estimation of profit and taxes;
3. Product and demand forecasting;
4. Increasing importance of finance decisions in marketing;
5. Managerial policies;
6. Negotiations for new contracts;
7. Marketing audit; and
ADVERTISEMENTS:
8. Goal setting of profit and worth maximisation.
Despite the importance and utility of accounting system, it must be borne in mind that it cannot provide solution to business problems. Sound judgment and experiences are qualities that have to be basically present in decision-maker with the aid of accounting information. Accounting is just an instrument which can help the marketer in avoiding guess work.
The major disadvantages of the method are:
(i) Lack of material control;
(ii) Monotonous collection of data;
(iii) Only financial measurement;
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iv) Lack of accuracy or preciseness;
(v) Wrong estimate of depreciation;
(vi) Post-mortem examination.
Computer Application in Accounting MkIS:
Accounting is an indispensable tool for providing information to the management, investors, creditors and other agencies regarding business affairs. In present day business environment, computerized accounting is being adopted rapidly, with the PCXT/AT compatible computers the accounting data are processed to derive the required information.
The computerized accounting systems are run with the use of finance, sales, inventory data. Before applying the automatic software, it is necessary to search and arrange previously all related figures in a sequential manner. On line computer processing in accounting provides up-to-date information.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
With the Electronic Data Processing (EDP) system the accounting data in a coded form known as input are fed into the computers so that processing of data may be made and desired results may be produced in the form of reports and documents known as output in code or plain language as desired by the investigator.
Before computerizing accounting data, the processing of transactions involves creation of an opening balance file at the beginning of a particular month. This file would contain the balance of all accounts in code order. Transactions from different sources such as cash, bank, and building are separately entered and validated to create a transaction file. This file is sorted in accounting code order.
The sorted file is superimposed on the opening balance file to generate a closing balance file. While the closing balance of the previous month becomes the opening balance for the following month, a set of outputs are printed. These are generally larger for the month.
The advantages of computer application are:
(i) Large savings in clerical labour;
(ii) Quick supply of relevant information;
ADVERTISEMENTS:
(iii) Accurate, reliable and latest information; and
(iv) Easy auditing.
On the other side following are the limitations of computers’ use in accounting: an initial huge investment; need of high professional talent; uneconomical for small business; unemployment; heavy repair and replacement charges; serious results of original stage errors. However, the recent past has witnessed a large scale growth of computerized accounting. To cope with the present day need more and more business enterprises should go for computer use to maximise the benefits.
According to Philip Kotler order shipping billing cycle is the heart of internal accounting system. It begins when orders are received from sales representatives, dealers and customers. The order department prepares invoices in multi copies and transmits them to various departments within the firm.
The goods are shipped to the buyer, and billing documents are multi copied and sent. Each and every firm should try to carry out these functions with maximum speed and accuracy. Sales representatives or dealers are supposed to dispatch their order immediately or as soon as possible.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The order department should send goods as earliest and the bills and other documents should be prepared and sent quickly. The computer can be helpful to expedite these functions. Turgen F. Ringer and Charles D. Howell reported a company study that the average elapsed time between the receipt and issuance of an order was cut from 62 hours to 30 hours while the costs of the cycle did not rise.
Other types of accounting MkIS suggested by T.C. Kelly are as follows:
1. Customer billing;
2. Sales activity;
3. Stock availability; and
4. Product costs.
P. Kotler has suggested some concrete points for using internal accounting system. Management should create such system which may provide current and enough statistical data. The confusion, doubt, prejudice, inclination and ambiguity should be avoided by sophisticated information.
For economic feasibility, accounting information planning committee may be appointed which interviews a cross-section of marketing executives, product managers, sales executives, sales representatives and others, after receiving the information the business undertakings should reconcile what information executives would like to have, what executives really need, and what is economically feasible for effectives managerial decision.
Components of Marketing Information System # 2. Marketing Intelligence System:
Marketing intelligence is the ‘current’ that keeps the vires of marketing management alive. Victory of marketing depends highly upon the executive’s ability to evaluate such things as size, location and attributes of various market environment for products, the nature of present and potential consumers reflecting in market segments their needs and desires, their buying habits and preferences, competition strengths and weakness, activities and plans and trend in market forces.
Marketing intelligence system is the way by which marketing executives are kept informed about present changing conditions of external and internal business positions. Internal accounting system supplies executives with past data, the marketing intelligence system provides executive the future’s expected data. It is the set of procedures and sources used by executives to obtain their everyday information about pertinent developments in the marketing environment.
Sources of Marketing Intelligence:
a. Official publications of the central, state and the local governments.
b. Official publications of the foreign countries’ governments or international bodies like U.N.O. and its subsidiary bodies, SAARC, Commonwealth of Nations and others.
c. Reports and publications of trade associations, chambers of commerce, banks, cooperative societies, stock and produce exchanges, trade unions etc.
d. Technical trade journals like the Indian Journal of Marketing, Marketology, Capital Wall Street Journal, New York Times, the books and newspapers.
e. Reports submitted by economists, university bureaus, and various associations.
f. Direct talking or indirect viewing by customers, suppliers, distributors, managers, employees, public etc.
g. Purchase of information from outside intelligence agency.
h. Establishing own marketing intelligence centres for information circulation.
Generally firms rely on sales people, suppliers, distributors and agents for intelligence MkIS. Salespeople are the best-fitted intelligence source. They are the ‘eyes and ears’ for company’s knowledge. They are in constant touch with general public and dealers. But for gaining maximum advantage sales people must be specially trained for expertised intelligence gathering.
The firm may hire of appoint full—time experts for active intelligence collection. Even the firm may purchase data from marketing intelligence centres. The Business Week of August 4, 1975 entitled an article, ‘Business Sharpens Its Spying Techniques’ and observed that, “with business more complex and the economic climate so uncertain, corporators are becoming for more sophisticated at scrutinizing the competition. Direct mailers, cataloguers, printers and lithographers were cited as popular leaves of information about competitors’ products. One marketing manager claimed that in the electronics industry, “tactics for keeping track of the competition are at times sneaky, may be even immoral or unethical.” Such strict precautions have become the rule of many fashion and high technological industries.
Components of Marketing Information System # 3. Marketing Research System:
The role of marketing research is advisory in marketing field. Marketing research is a formal mean of obtaining information to be used in marketing decision-making. Marketing research is the collection and interpretation of facts that help marketers to get product’ more efficiently into the hands of the customers. The American Marketing Association defines marketing research as- “The systematic gathering, recording, analysis of data about problems relating to the marketing of goods and services.”
According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing research is the systematic design collection analysis, and reporting of data and findings relevant to a specific marketing situation facing the company.” The information gathered by the marketing research reduces the risk and uncertainty in decision-making. The creativity and imagination are essential ingredients in today’s decisions.
The procedure and climate for conducting marketing research are taken directly from scientific method ensuring that marketing research will produce information that is verificable, systematic, communicable, explanatory and predictive. In fact, marketing research is a part of social research and has acquired great academic status. It should not be confused with market research.
Market research is only a component of marketing research, which strictly means study of the market itself to establish its size, growth or dealing, the factor affecting it, the number of competitors active in it, their market shares, the prices in market, and so on. Market research conveys narrower meaning than marketing research which covers the entire existing process and not merely the market.
Marketing research covers the entire broad area of marketing management. It is a dynamic and continuous scientific study having a wide coverage. It begins even when production is at planning stage and continues throughout the life time of business. It is a great important managerial tool, which can be applied in every aspect of marketing as product, market, sales, distribution, advertising and so on.
Thus, management should treat marketing research as an important and permanent branch, and not as one project at a time manner. Marketing researches have close association with decision makers in order to play an effective and educational role. Despite the importance of marketing research it must be borne in mine that it could not provide a solution to every business problem.
It is only a tool for avoiding guess work. But it is not an exact science. Sound business judgment and experiences are the basic qualities for the successful decision-maker. Marketing research serves as a coordinating link between marketing and other functional areas such as manufacturing, engineering, finance and accounting. Marketing research has pioneered the move toward a broader view of marketing.
Components of Marketing Information System # 4. Marketing Science System:
Several large companies have developed advanced techniques for analysing marketing data and problems. The objective approach of establishing cause and effect relationship to predict about marketing problems is a sophisticated technique of MkIS.
The development of statistical analysis and mathematical models based on computers and econometrics have emerged a new dimension to solve media selection, to evaluate new product acceptance and to weigh sales and pricing alternatives. Marketing science may provide regular and continuous base for marketing investigations like, “why did that happen?” and “what will happen if….?”
To know whether marketing is a ‘science’ or not; we must know the meaning of science. Science is generally meant a systematised and organised body of knowledge. But in specific sense science is a body of principles, theories or law. Theory establishes a cause and effect relationship between two events so that if we know one event ’cause’ we can predict the behaviour of other event ‘effect’.
The main attributed of science are:
(a) Objective approach based on facts and logics;
(b) Precise power to explain cause and effect relationship;
(c) Good capacity to predict the exactness of theory or low;
(d) Use of scientific method.
Science is built up of facts as a house is built up of stones, but an accumulation of facts is no more a science than a heap of stones is a house. Science is a system of facts and principles covering a subject. It is a rich fund of knowledge founded on experience and research that has set generalisations and universal acceptance.
Marketing, like other any natural science does seek to build a body of valid laws and principles, e.g. the rise and fall in the customer income directly affects the sales potential in any market. The higher the prices the lower will be consumer demand. There is substantial body of knowledge and principles about marketing which has common acceptance, such generalisations render marketing as a science.
But the laboratory of marketing is the whole business world and the element of study is the changing consumer behaviour. So marketing cannot be as exact as the formula of natural sciences like physics, chemistry or mathematics. Marketing is a social science which deals with the mental and economic problems of individuals as well as group organisations.
Marketing is more of an art than a science. The successful marketing practices depend upon the skill and judgment of the person concerned with marketing and cannot be reduced to an organised body of theories and principles.
According to Boyd and Westfall, following problems are faced in application of scientific method to marketing problems:
(a) The subject of investigation is a very complex subject—human being,
(b) This complexity of subject combined with the use of relatively crude measuring devices, makes very difficult to get accurate measurement,
(c) The process of measuring human may cause them to change,
(d) It is difficult to use experiments in various marketing problems,
(e) Since peoples, attitudes change frequently, it is very hard to predict accurately, and
(f) Since the measuring devices available are relatively subjective, it is hard to keep marketing study completely objective.
Statistical Techniques of Marketing Science:
Marketing scientists do use statistical techniques for explaining, predicting and controlling the information. Statistical analysis is a collection of some advanced statistical tools for measuring the intensity or degree of relationship between two or more variables.
This analysis provides purposeful information from data for decision-making, some common statistical techniques for analysis and interpretation are central tendency measures, measures of dispersion, skewness, moments, and kurtosis. Beyond these the investigator may use various advanced techniques described in the degree of association between variables.
1. Association of Attributes:
It refers to such techniques by which we measure the relationship between two such phenomena whose size cannot be measured and where we can only find the presence or absence of any attribute.
As a measure of the intensity of association between two attributes A and B, Gudny Yule has given the coefficient of association (Q) defined as follows:
(i) If A and B are independent then Q = 0;
(ii) If A and B are completely associated then Q = +1;
(iii) If A and B are completely dissociated then
Hence Q varies from -1 to +1.
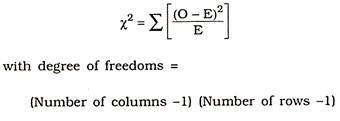
2. Chi-Square (χ 2) Test:
Chi-Square test (Chi pronounced as KI) is a non-parametric technique that can be used for determining the probability that differences in the expected and observed number of cases are significant or insignificant. Except three parametric tests (Z-test, t-test and F-test) chi-square test is a very powerful test for testing goodness of fit.
The value of chi-square is computed by the formula:
In this formula O is the observed value and E is the expected value. This test is applied for testing the significance of the discrepancy between theory and experiment given by Prof. Karl Pearson in 1900 and is known as Chi-Square test of goodness of fit.
3. Correlation Analysis:
According to Croxton and Cowden, “when the relationship is of a quantitative nature, the appropriate statistical tool for discovering and measuring the relationship and expressing it in a brief formula in known as correlation.” The word correlation is used in the sense of mutual dependence of two or more variables indicating cause and effect relationship between them.
The correlation can be:
(i) Positive or negative,
(ii) Simple, multiple and partial, and
(iii) Linear and non-linear.
When the values of variables move in same direction so that an increase in the value of one variable is associated with an increase in the value of the other variable also, and decrease in the value of one variable is associated with the decrease in the value of the other variable also, correlation is said to be positive. Contrary to it is called negative correlation. Generally, price and supply are positively correlated; and the price and demand are negatively, correlated.
In simple or bivariate correlation the relationship between two variables are studied; but sometimes when there is interrelation between three or more variables and the value of one variable may be influenced by many others the relationship is studied by multiple correlation. In partial correlation though more than two factors are involved but correlation is studied only between two eliminating the others.
When the variation in the value of variables are in constant ratio, the correlation is said to be linear. For example if with 15% increase in advertising expenses each time results 20% increase in sales volume; then there is linear relationship. But mostly in marketing field, such relationships are very rare and ratios are fluctuating resulting in non-linear correlation.
The various methods of correlation analysis are:
(i) Scatter diagram;
(ii) Correlation graph;
(iii) Karl Pearson’ coefficient of correlation;
(iv) Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient;
(v) Coefficient of concurrent deviation; and
(vi) Method of least squares.
As a measure of degree of relationship between two variables, Karl Pearson (1867-1936) a British Biometrician, developed the most popular method called correlation coefficient.
The formula for calculating coefficient of correlation (r) is as follows:
Components of Marketing Information System 4. Regression Analysis:
The term ‘regression’ literally means stepping back towards the average. It was first used by a British Biometrician, Sir Francis Galton (1822-1911), in connection with the inheritance of stature. Galton found that the offspring of abnormally tall or short parents tend to ‘regress’ or step back to the average population height.
But now the term regression is used in statistics as going back or returning the variables toward the mean. Regression analysis is a mathematical measure of the average relationship between two or more variables in terms of original units of the data.
For studying marketing problems regression analysis is very purposeful for predicting the unknown future values of any variable from the known value. The regression study of two variables is called simple regression analysis and with three or more variables at a time is called multiple regression analysis.
Regression can be studied either graphically or algebraically. Under graphic method linear regression lines can be drawn by free hand or least squares method. In algebraic method regression equations are expressed on the place of regression lines. In bivariate distribution if Y is dependent and X is independent variable then the regression equation of Y on X be
Y = a + bX
And, if X is dependent and Y is independent variable then the regression equation of X on Y be
X = a + bY
Regression Equation of X on Y
Where X̅ denotes the actual mean of X series and Y̅ denotes the actual mean of Y series, r denotes coefficient of correlation between X and Y series.
Correlation coefficient is the geometric mean between the both regression coefficients.
5. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA):
According to Prof. R.A. Fisher, analysis of variance is the, “separation of variance ascribable to one group of causes from the variance ascribable to other group.” By this technique the total variation in the simple data is expressed as the sum of its positive components where each of the components is a measure of the variation due to some specific independent factors.
The ANOVA consists the estimation of the amount of variation due to each of the independent factors separately and then comparing these estimates due to assignable factors with the estimate due to chance factor, the latter being known as experimental error. Two models intuitive and mathematical are used in ANOVA technique.
R.A. Fisher developed an elaborate technique for analysing the variations of two or more series for the purpose of studying their attributes. Variance is the square of the standard deviation of a series and given an idea about the variability of the values of variables from the mean. The analysis of variance is very effective tool for analysing data.
6. Other Techniques:
(a) Discriminant Analysis:
Under this tool the dependent variable is classified into two or more categories using a set of predictor variable. The discriminant equation is used to forecast what new attributes are important for success in comparison to other concerns.
(b) Factor Analysis:
It is a statistical tool for marketing scientist to discover a few basic factors that may explain the inter-correlations among larger number of variables. The purpose of factor analysis is to summarize large number of variables into small number called, factors.
(c) Cluster Analysis:
The objective of cluster analysis is to make numerical taxonomy into subgroups or clusters which are relatively homogeneous’. Cluster analysis has been used for testing various marketing problems as to make market segments of peoples group to examine similarities among different countries market, to determine competition patterns, to select appropriate market or product or place. Several cluster techniques are available depending on the multi-dimensional data as nominal, ordinal and interval.
Marketing executives can apply various models developed by operation researchers for marketing decisions as descriptive, graphical, verbal and mathematical. A marketing executive may build Markov process, queuing, differential calculus, mathematical programming, game theory, logical flow, feedback system, decision tree, network planning, casual, linear, and deterministic, stochastic, static models to solve marketing problems.
Each model consists of a set of interrelated variables which help marketers for effective decision-making. In the last thirty years, marketing scientists have developed a great number of models for different crucial decisions relating to pricing, strategic planning, market measurement, targeting, packaging, communication and others.